Nitric Oxide Analysis
Nitric oxide (NO) has been administered therapeutically in concentrations
of 1 to 100 parts per million (ppm) as a pulmonary vasodilator. Continuous monitoring
of the inhaled concentration can be accomplished using relatively inexpensive but
specific and stable electrochemical detectors.[164]
[165]
There has been interest in monitoring endogenously
produced NO in exhaled gas.[166]
Analysis of exhaled
NO waveforms, in which end-tidal NO concentrations are typically on the order of
1 to 100 parts per billion (ppb), can be satisfactorily performed only by using mass
spectrometry or rapid-response chemiluminescence analyzers,[167]
which typically have a resolution of 0.1 ppb or less. Gaseous chemiluminescence
analyzers usually rely on the chemical reaction of NO with ozone (O3
)
to produce nitrogen dioxide (NO2
). Some NO2
molecules are
produced in an excited state (NO2
*).[168]
When NO2
* then spontaneously reverts to its ground state, a photon
is emitted. This emitted chemiluminescence signal, which has a wavelength at maximum
intensity at approximately 1200 nm, can be detected using a photomultiplier.
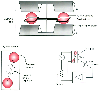 Figure 36-13
Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer. Two sealed spheres filled
with nitrogen are suspended in a magnetic field. Nitrogen (N2
) is slightly
diamagnetic, and the resting position of the beam is such that the spheres are displaced
away from the strongest portion of the field. If the surrounding gas contains oxygen,
the spheres are pushed further out of the field by the relatively paramagnetic oxygen.
The magnitude of the torque is related to the paramagnetism of the gas mixture and
is proportional to the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2
).
Movement of the dumbbell is detected by photocells, and a feedback current is applied
to the coil encircling the spheres, returning the dumbbell to the zero position.
The restoring current and output voltage are proportional to the PO2
.
(Courtesy of Servomex Co., Norwood, MA.)
Figure 36-13
Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer. Two sealed spheres filled
with nitrogen are suspended in a magnetic field. Nitrogen (N2
) is slightly
diamagnetic, and the resting position of the beam is such that the spheres are displaced
away from the strongest portion of the field. If the surrounding gas contains oxygen,
the spheres are pushed further out of the field by the relatively paramagnetic oxygen.
The magnitude of the torque is related to the paramagnetism of the gas mixture and
is proportional to the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2
).
Movement of the dumbbell is detected by photocells, and a feedback current is applied
to the coil encircling the spheres, returning the dumbbell to the zero position.
The restoring current and output voltage are proportional to the PO2
.
(Courtesy of Servomex Co., Norwood, MA.)
NO2
in the original gas sample reacts slowly with O3
, even
if it is present in high concentration. Chemiluminescence analyzers measure NO2
concentration by first converting it to NO in a high-temperature reactor chamber.
 Figure 36-13
Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer. Two sealed spheres filled
with nitrogen are suspended in a magnetic field. Nitrogen (N2
) is slightly
diamagnetic, and the resting position of the beam is such that the spheres are displaced
away from the strongest portion of the field. If the surrounding gas contains oxygen,
the spheres are pushed further out of the field by the relatively paramagnetic oxygen.
The magnitude of the torque is related to the paramagnetism of the gas mixture and
is proportional to the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2
).
Movement of the dumbbell is detected by photocells, and a feedback current is applied
to the coil encircling the spheres, returning the dumbbell to the zero position.
The restoring current and output voltage are proportional to the PO2
.
(Courtesy of Servomex Co., Norwood, MA.)
Figure 36-13
Paramagnetic oxygen analyzer. Two sealed spheres filled
with nitrogen are suspended in a magnetic field. Nitrogen (N2
) is slightly
diamagnetic, and the resting position of the beam is such that the spheres are displaced
away from the strongest portion of the field. If the surrounding gas contains oxygen,
the spheres are pushed further out of the field by the relatively paramagnetic oxygen.
The magnitude of the torque is related to the paramagnetism of the gas mixture and
is proportional to the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2
).
Movement of the dumbbell is detected by photocells, and a feedback current is applied
to the coil encircling the spheres, returning the dumbbell to the zero position.
The restoring current and output voltage are proportional to the PO2
.
(Courtesy of Servomex Co., Norwood, MA.)