 |
 |
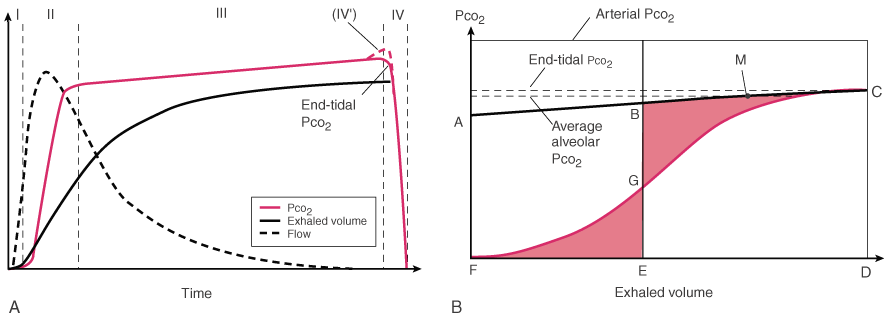
Figure 36-17
Time and volume capnographs. A,
Expired PCO2
versus time (i.e., standard
time capnogram). The waveform is conventionally subdivided into phases. During
phase I, exhaled gas from the large airways has a PCO2
= 0. Phase II is the transition between airway and alveolar gas. Phase III (i.e.,
alveolar plateau) is normally flat, but in the presence of V̇A/ mismatching, it has a positive slope. The down slope of the capnogram at the onset
of inspiration is usually referred to as phase IV, but there is sometimes a terminal
increase in the slope associated with the onset of airway closure (dashed
line labeled IV'). This corresponds to the terminal upstroke seen in
single inert gas washout curves, referred to in that setting as phase IV.[322]
The PCO2
value at the end of exhalation
is referred to as the end-tidal PCO2
(PETCO2
).
Also shown are the exhaled gas flow rate and volume. B,
Volume capnogram. In this form of the capnogram, exhaled PCO2
is plotted against exhaled volume. Mixed expired PCO2
can be measured for each breath as the area under the capnogram. Total physiologic
dead space (VDS PHYS) can there fore be measured
using arterial PCO2
and Equation 12 (Bohr
equation, assuming PACO2
= PACO2
).
Line AC is drawn tangent to the terminal portion of the alveolar plateau. Vertical
line BE is constructed such that the two shaded areas (EDG and BCG) are equal in
area. FE therefore represents anatomic dead space (VDS ANAT),
[323]
which includes the volume in the trachea and
large airways and any volume within a breathing circuit in which exhaled gas is rebreathed,
such as the endotracheal tube, passive humidification device, or Y-piece. Alveolar
dead space (VDS ALV)[323]
can therefore be calculated as the difference between VDS PHYS
and VDS ANAT.[324]
Because the area of trapezoid BCDE is equal to the volume of CO2
exhaled
per breath, the mean (or average) alveolar PCO2
is the value at the midpoint of segment BC (point P).[324]
mismatching, it has a positive slope. The down slope of the capnogram at the onset
of inspiration is usually referred to as phase IV, but there is sometimes a terminal
increase in the slope associated with the onset of airway closure (dashed
line labeled IV'). This corresponds to the terminal upstroke seen in
single inert gas washout curves, referred to in that setting as phase IV.[322]
The PCO2
value at the end of exhalation
is referred to as the end-tidal PCO2
(PETCO2
).
Also shown are the exhaled gas flow rate and volume. B,
Volume capnogram. In this form of the capnogram, exhaled PCO2
is plotted against exhaled volume. Mixed expired PCO2
can be measured for each breath as the area under the capnogram. Total physiologic
dead space (VDS PHYS) can there fore be measured
using arterial PCO2
and Equation 12 (Bohr
equation, assuming PACO2
= PACO2
).
Line AC is drawn tangent to the terminal portion of the alveolar plateau. Vertical
line BE is constructed such that the two shaded areas (EDG and BCG) are equal in
area. FE therefore represents anatomic dead space (VDS ANAT),
[323]
which includes the volume in the trachea and
large airways and any volume within a breathing circuit in which exhaled gas is rebreathed,
such as the endotracheal tube, passive humidification device, or Y-piece. Alveolar
dead space (VDS ALV)[323]
can therefore be calculated as the difference between VDS PHYS
and VDS ANAT.[324]
Because the area of trapezoid BCDE is equal to the volume of CO2
exhaled
per breath, the mean (or average) alveolar PCO2
is the value at the midpoint of segment BC (point P).[324]
 |
![]() mismatching, it has a positive slope. The down slope of the capnogram at the onset
of inspiration is usually referred to as phase IV, but there is sometimes a terminal
increase in the slope associated with the onset of airway closure (dashed
line labeled IV'). This corresponds to the terminal upstroke seen in
single inert gas washout curves, referred to in that setting as phase IV.[322]
The PCO2
value at the end of exhalation
is referred to as the end-tidal PCO2
(PETCO2
).
Also shown are the exhaled gas flow rate and volume. B,
Volume capnogram. In this form of the capnogram, exhaled PCO2
is plotted against exhaled volume. Mixed expired PCO2
can be measured for each breath as the area under the capnogram. Total physiologic
dead space (VDS PHYS) can there fore be measured
using arterial PCO2
and Equation 12 (Bohr
equation, assuming PACO2
= PACO2
).
Line AC is drawn tangent to the terminal portion of the alveolar plateau. Vertical
line BE is constructed such that the two shaded areas (EDG and BCG) are equal in
area. FE therefore represents anatomic dead space (VDS ANAT),
[323]
which includes the volume in the trachea and
large airways and any volume within a breathing circuit in which exhaled gas is rebreathed,
such as the endotracheal tube, passive humidification device, or Y-piece. Alveolar
dead space (VDS ALV)[323]
can therefore be calculated as the difference between VDS PHYS
and VDS ANAT.[324]
Because the area of trapezoid BCDE is equal to the volume of CO2
exhaled
per breath, the mean (or average) alveolar PCO2
is the value at the midpoint of segment BC (point P).[324]
mismatching, it has a positive slope. The down slope of the capnogram at the onset
of inspiration is usually referred to as phase IV, but there is sometimes a terminal
increase in the slope associated with the onset of airway closure (dashed
line labeled IV'). This corresponds to the terminal upstroke seen in
single inert gas washout curves, referred to in that setting as phase IV.[322]
The PCO2
value at the end of exhalation
is referred to as the end-tidal PCO2
(PETCO2
).
Also shown are the exhaled gas flow rate and volume. B,
Volume capnogram. In this form of the capnogram, exhaled PCO2
is plotted against exhaled volume. Mixed expired PCO2
can be measured for each breath as the area under the capnogram. Total physiologic
dead space (VDS PHYS) can there fore be measured
using arterial PCO2
and Equation 12 (Bohr
equation, assuming PACO2
= PACO2
).
Line AC is drawn tangent to the terminal portion of the alveolar plateau. Vertical
line BE is constructed such that the two shaded areas (EDG and BCG) are equal in
area. FE therefore represents anatomic dead space (VDS ANAT),
[323]
which includes the volume in the trachea and
large airways and any volume within a breathing circuit in which exhaled gas is rebreathed,
such as the endotracheal tube, passive humidification device, or Y-piece. Alveolar
dead space (VDS ALV)[323]
can therefore be calculated as the difference between VDS PHYS
and VDS ANAT.[324]
Because the area of trapezoid BCDE is equal to the volume of CO2
exhaled
per breath, the mean (or average) alveolar PCO2
is the value at the midpoint of segment BC (point P).[324]
