ALTERATIONS IN NEUROREGULATORS ASSOCIATED WITH ANESTHESIA
The list of CNS transmitters is rapidly expanding. In addition
to the classic transmitters (e.g., acetylcholine), endogenous amino acids and peptides
may act as neurotransmitters or modulate the action of other neurotransmitters.
The postsynaptic action of neurotransmitters may result in the formation of second
messengers that
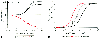 Figure 4-7
A, Effects of halothane
(Hal), enflurane (Enf), and the convulsant hexafluorodiethyl ether [flurothyl] (HFE)
on current responses evoked by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (3 ×
10−6
M) application to dissociated central nervous system
neurons of the rat. Responses are normalized to the peak current induced by 3
× 10−6
M GABA alone. B,
The GABA concentration-response curve is shifted to the left by halothane and to
the right by HFE. Peak response was normalized to that evoked by 3 ×
10−6
M GABA (asterisk).
(Adapted from Wakamori M, Ikemoto Y, Akaike N: Effects of two volatile
anesthetics on the excitatory and inhibitory amino acid responses in dissociated
CNS neurons of the rat. J Neurophysiol 66:2014, 1991.)
Figure 4-7
A, Effects of halothane
(Hal), enflurane (Enf), and the convulsant hexafluorodiethyl ether [flurothyl] (HFE)
on current responses evoked by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (3 ×
10−6
M) application to dissociated central nervous system
neurons of the rat. Responses are normalized to the peak current induced by 3
× 10−6
M GABA alone. B,
The GABA concentration-response curve is shifted to the left by halothane and to
the right by HFE. Peak response was normalized to that evoked by 3 ×
10−6
M GABA (asterisk).
(Adapted from Wakamori M, Ikemoto Y, Akaike N: Effects of two volatile
anesthetics on the excitatory and inhibitory amino acid responses in dissociated
CNS neurons of the rat. J Neurophysiol 66:2014, 1991.)
mediate changes in neuronal transmission. Limited information is available concerning
the relationship between the levels of neuroregulators in the CNS and the inhaled
anesthetic requirement.
Acetylcholine
Inhaled anesthetics do not alter acetylcholine concentrations
in macroscopic structures (e.g., cortex) of rat brain[51]
but may increase or decrease[52]
acetylcholine content
in specific brain nuclei. Inhaled agents decrease acetylcholine turnover rate, and
the magnitude of the decrease varies with the brain region examined.[51]
Release of acetylcholine into rat cerebral cortex is suppressed by isoflurane and
sevoflurane but enhanced by nitrous oxide.[53]
Synthesis of acetylcholine in brain is impaired by inhaled agents and is associated
with an anesthetic-induced inhibition of choline uptake.[41]
Although the direct application of a cholinergic agonist to a discrete nucleus of
the rat brainstem reticular formation decreases halothane MAC,[54]
intrathecal or intraperitoneal injection of acetylcholine receptor antagonists has
little or no influence on isoflurane MAC in rats.[55]
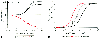 Figure 4-7
A, Effects of halothane
(Hal), enflurane (Enf), and the convulsant hexafluorodiethyl ether [flurothyl] (HFE)
on current responses evoked by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (3 ×
10−6
M) application to dissociated central nervous system
neurons of the rat. Responses are normalized to the peak current induced by 3
× 10−6
M GABA alone. B,
The GABA concentration-response curve is shifted to the left by halothane and to
the right by HFE. Peak response was normalized to that evoked by 3 ×
10−6
M GABA (asterisk).
(Adapted from Wakamori M, Ikemoto Y, Akaike N: Effects of two volatile
anesthetics on the excitatory and inhibitory amino acid responses in dissociated
CNS neurons of the rat. J Neurophysiol 66:2014, 1991.)
Figure 4-7
A, Effects of halothane
(Hal), enflurane (Enf), and the convulsant hexafluorodiethyl ether [flurothyl] (HFE)
on current responses evoked by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (3 ×
10−6
M) application to dissociated central nervous system
neurons of the rat. Responses are normalized to the peak current induced by 3
× 10−6
M GABA alone. B,
The GABA concentration-response curve is shifted to the left by halothane and to
the right by HFE. Peak response was normalized to that evoked by 3 ×
10−6
M GABA (asterisk).
(Adapted from Wakamori M, Ikemoto Y, Akaike N: Effects of two volatile
anesthetics on the excitatory and inhibitory amino acid responses in dissociated
CNS neurons of the rat. J Neurophysiol 66:2014, 1991.)