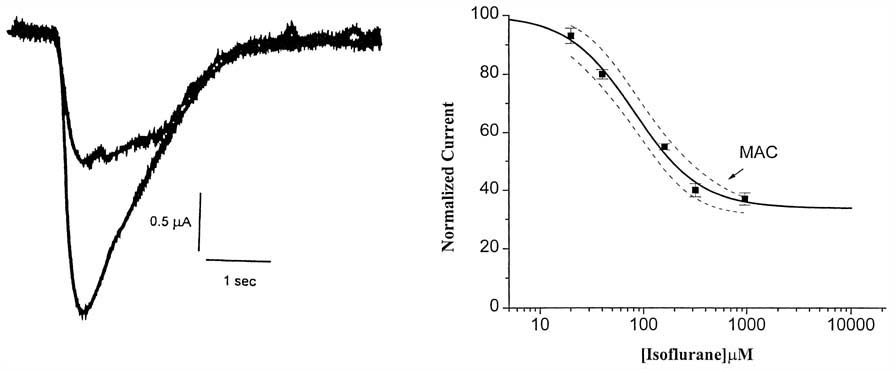
Figure 4-13
The figure on the left shows the current from an oocyte
that expresses the predominant nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtype (α4β2)
found in the central nervous system. Isoflurane (320 µM) reduces the peak
current obtained in response to 1 µM acetylcholine from 2.4 µA to 1.1
µA (46% of control). The graph on the right shows the dose-response curve
of the inhibition of α4β2 receptor subtype current by isoflurane. Notice
that some inhibition of receptor function occurs even at an isoflurane concentration
of about 0.1 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC). (Adapted from Flood P,
Ramirez-Latorre J, Role L: α4β2 Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
in the central nervous system are inhibited by isoflurane and propofol, but α7-type
nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are unaffected. Anesthesiology 86:859, 1997.)