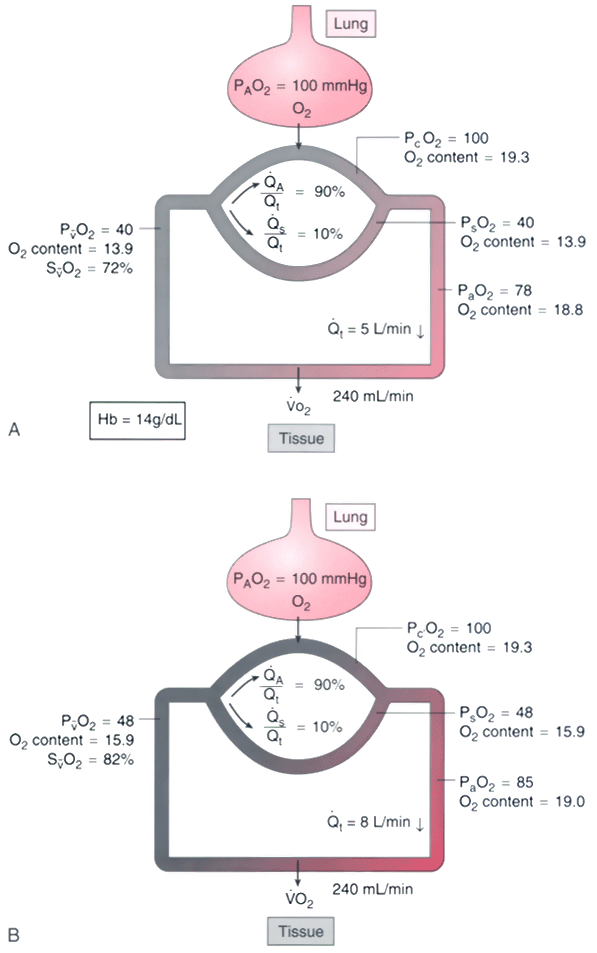
Figure 36-4
Effect of cardiac output on PO2
.
A, Arterial and mixed venous O2
tension
and content are shown at a cardiac output of 5 L/min. B,
Assuming a constant V̇O2
, an increase
in cardiac output to 8 L/min increases the PaO2
from 78 to 85 mm Hg. This occurs because Sv̄O2
increases at higher cardiac output. The resulting increase in O2
content
of the shunted blood (here assumed to be 10% of cardiac output) then raises arterial
O2
content and PaO2
. PO2
values are in mm Hg, and O2
content is in mL/dL.