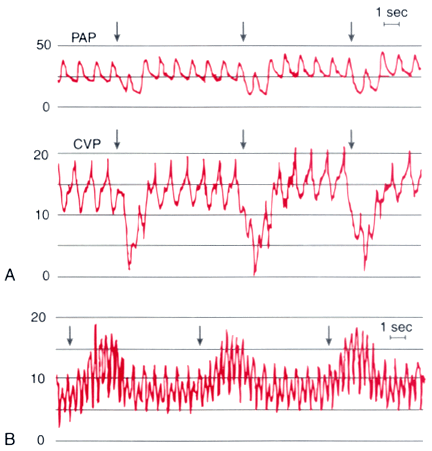
Figure 32-27
Respiratory influences on the measurement of central
venous pressure (CVP). A, During spontaneous ventilation,
the onset of inspiration (arrows) causes a reduction
in intrathoracic pressure that is transmitted to both the CVP and the pulmonary artery
pressure (PAP) waveforms. CVP should be recorded at end-expiration (mean CVP, 14
mm Hg). B, During positive-pressure ventilation,
the onset of inspiration (arrows) causes an increase
in intrathoracic pressure. CVP is still recorded at end-expiration (mean CVP, 8
mm Hg). (Redrawn from Mark JB: Atlas of Cardiovascular Monitoring. New
York, Churchill Livingstone, 1998, Figs. 16-1 and 16-2.)