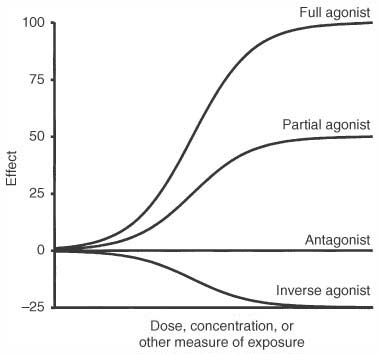
Figure 3-23
Effects of various types of ligands on receptor responses.
A full agonist produces complete (100%) activation of a receptor at high concentrations,
whereas partial agonist binding results in less than 100% activation, even at very
high concentrations. A neutral antagonist has no activity of its own. Inverse agonists
can be thought of as "superantagonists" because binding of these ligands produces
a response below the baseline response measured in the absence of drug. If the physiologic
effect of the baseline levels of activated receptor (R*) is small, antagonists
and inverse agonists may not be clinically distinguishable.