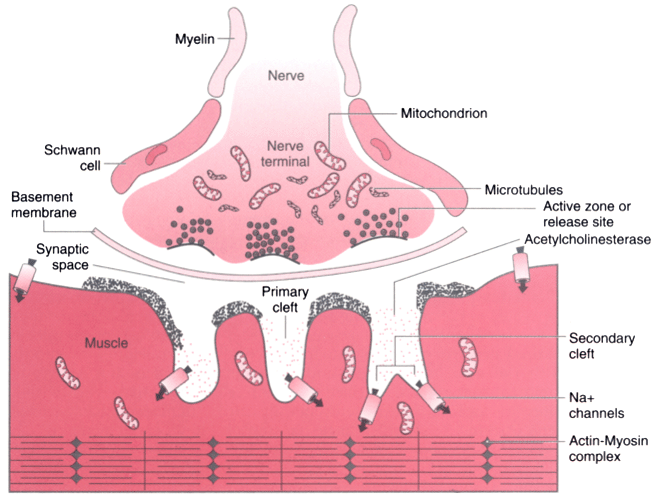
Figure 22-1
Adult neuromuscular junction with the three cells that
constitute the synapse: the motor neuron (i.e., nerve terminal), muscle fiber, and
Schwann cell. The motor neuron from the ventral horn of the spinal cord innervates
the muscle. Each fiber receives only one synapse. The motor nerve loses its myelin
to terminate on the muscle fiber. The nerve terminal, covered by a Schwann cell,
has vesicles clustered about the membrane thickenings, which are the active zones,
toward its synaptic side and mitochondria and microtubules toward its other side.
A synaptic gutter, made up of a primary and many secondary clefts, separates the
nerve from the muscle. The muscle surface is corrugated, and dense areas on the
shoulders of each fold contain acetylcholine receptors. The sodium channels are
present at the clefts and throughout muscle membrane.