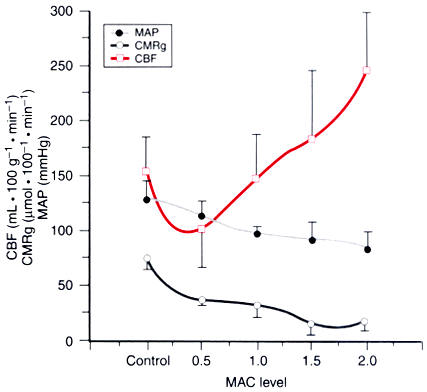
Figure 21-10
Relationship between changes in the cerebral metabolic
rate for glucose (CMRg) and cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the motor-sensory cortex
in rats during isoflurane anesthesia. Most of the CMR suppression caused by isoflurane
had occurred by 1.0 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC), and in this concentration
range CBF is not increased. Thereafter, additional isoflurane causes little further
reduction in CMR, and cerebral vasodilation occurs. These data (±SD), from
Maekawa and colleagues,[27]
suggest the importance
of metabolic coupling in determining the CBF effects of isoflurane.