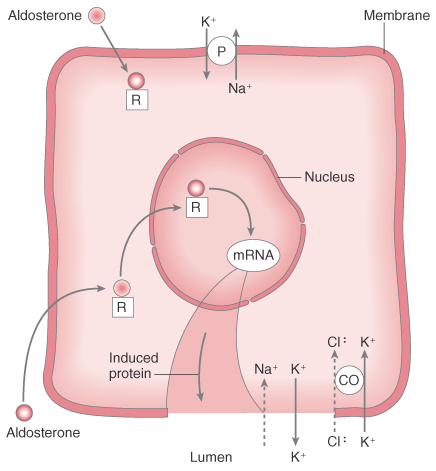
Figure 20-16
Action of aldosterone. Aldosterone enters the distal
tubular cytoplasm, attaches to a receptor, and then migrates to the nucleus, where
it induces the formation of messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA in turn induces the synthesis
of a protein that enhances the permeability of the apical (luminal) membrane to sodium
and potassium. Reabsorption of sodium stimulates the basolateral membrane Na-K-ATPase
pump, the intracellular concentration of potassium rises, and it follows its concentration
gradient out into the lumen. The net effect of aldosterone's action is sodium reabsorption
and potassium loss. CO, cotransporter (= symporter); P, sodium-potassium-ATPase
pump; R, receptor. (Redrawn from Wingard LB, Brody TM, Larner J, Schwartz
A: Diuretics: Drugs that increase excretion of water and electrolytes. In
Wingard LB, Brody TM, Larner J, Schwartz A [eds]: Human Pharmacology: Molecular-to-Clinical.
London, Wolfe, 1991, p 249.)