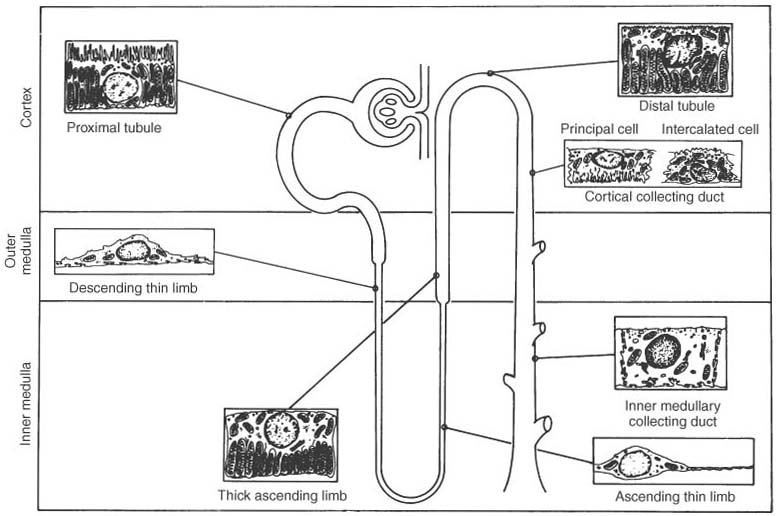
Figure 20-6
Structure-function relationships in the renal tubule.
The most metabolically active components of the tubule are the proximal tubule,
the thick ascending loop of Henle, and the first part of the distal tubule. Their
cells are large, and the capillary surface (basolateral membrane) has many invaginations
rich in mitochondria. The cells of the proximal tubule have a brush border on the
luminal surface (apical cell membrane), whereas the cells of the descending and thin
ascending loops of Henle are flattened with few mitochondria. The second part of
the distal tubule and collecting duct are intermediate in nature. The intercalated
cells of the distal tubule have many mitochondria, whereas the principal cells have
few. (From Stanton BA, Koeppen BM: Elements of renal function. In
Berne RM, Levy MN [eds]: Physiology, 4th ed. St Louis, CV Mosby, 1998, pp 677–698.)