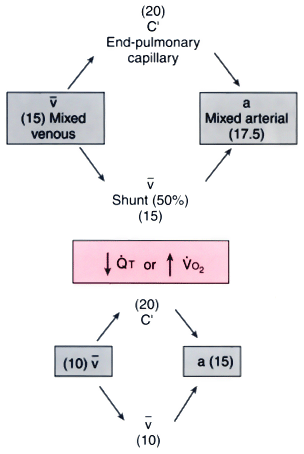
Figure 17-28
The equivalent circuit of the pulmonary circulation in
a patient with a 50% right-to-left shunt. Oxygen content is in mL/100 mL of blood
(vol%). A decrease in cardiac output ( T) or
an increase in O2
consumption (V̇O2
)
can cause a decrease in mixed venous oxygen content (from 15 to 10 vol% in this example),
which in turn will cause a decrease in the arterial content of oxygen (from 17.5
to 15.0 vol%). In this 50% shunt example, the decrease in mixed venous oxygen content
was twice the decrease in arterial oxygen content.
T) or
an increase in O2
consumption (V̇O2
)
can cause a decrease in mixed venous oxygen content (from 15 to 10 vol% in this example),
which in turn will cause a decrease in the arterial content of oxygen (from 17.5
to 15.0 vol%). In this 50% shunt example, the decrease in mixed venous oxygen content
was twice the decrease in arterial oxygen content.
![]() T) or
an increase in O2
consumption (V̇O2
)
can cause a decrease in mixed venous oxygen content (from 15 to 10 vol% in this example),
which in turn will cause a decrease in the arterial content of oxygen (from 17.5
to 15.0 vol%). In this 50% shunt example, the decrease in mixed venous oxygen content
was twice the decrease in arterial oxygen content.
T) or
an increase in O2
consumption (V̇O2
)
can cause a decrease in mixed venous oxygen content (from 15 to 10 vol% in this example),
which in turn will cause a decrease in the arterial content of oxygen (from 17.5
to 15.0 vol%). In this 50% shunt example, the decrease in mixed venous oxygen content
was twice the decrease in arterial oxygen content.