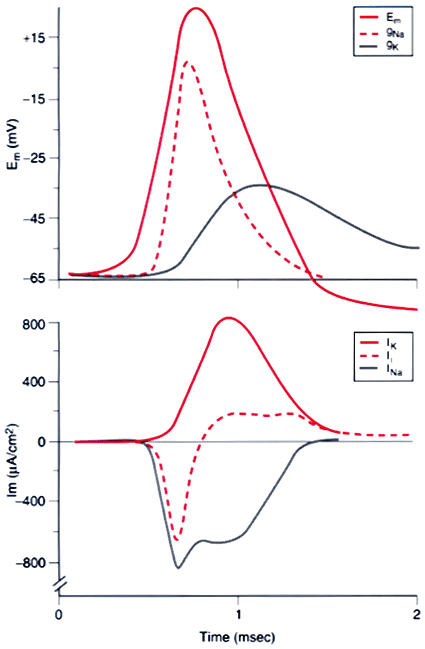
Figure 14-6
The membrane potential (Em
) and the voltage-gated
ionic conductance of sodium (gNa
) and potassium (gK
) that determine
the corresponding membrane currents (INa
and IK
) during a propagated
action potential. Modeled from the original studies of Hodgkin and Huxley on the
squid giant axon (see Hodgkin[8]
), these relationships
hold for almost all invertebrate and vertebrate nerve fibers. The direction of the
total ionic current (Ii
), which is the sum of INa
) and IK
,
is inward (negative values) for the depolarizing phase of the action potential and
outward (positive values) for the repolarizing phase.