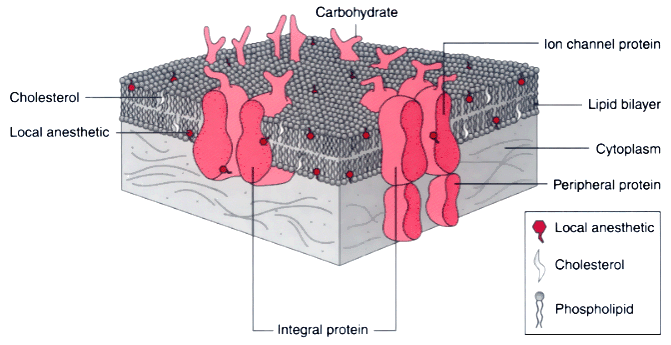
Figure 14-5
A typical plasma membrane has at its core the lipid bilayer,
which is composed of phospholipids and cholesterol molecules (in about a 5:1 ratio)
embedding the membrane integral proteins. These proteins are most often glycosylated
by extracellular carbohydrates and include receptors and ion channels essential for
intercellular communication. "Peripheral proteins" regulate the functions of membrane
proteins, chaperone them to the plasma membrane, and stabilize them in the cell through
interactions with both the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. Probable membrane
locations and protein sites for local anesthetics are also shown.