|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
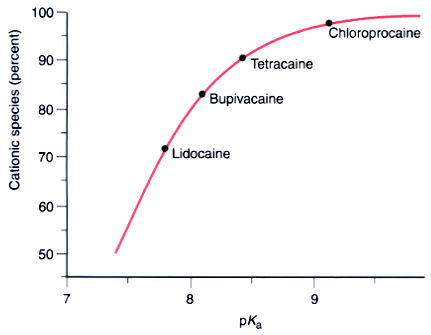
Figure 14-2
The fraction of local anesthetic in the protonated, cationic
form in aqueous solution at physiologic pH (7.4) as a function of the pKa
of the drug. The drug with the lowest pKa
,
lidocaine, has the smallest fraction of its molecules protonated and the largest
in the neutral form, and vice versa for the local anesthetic with the highest pKa
,
chloroprocaine. Individual drug molecules become protonated and deprotonated in
thousandths of a second in solution.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|