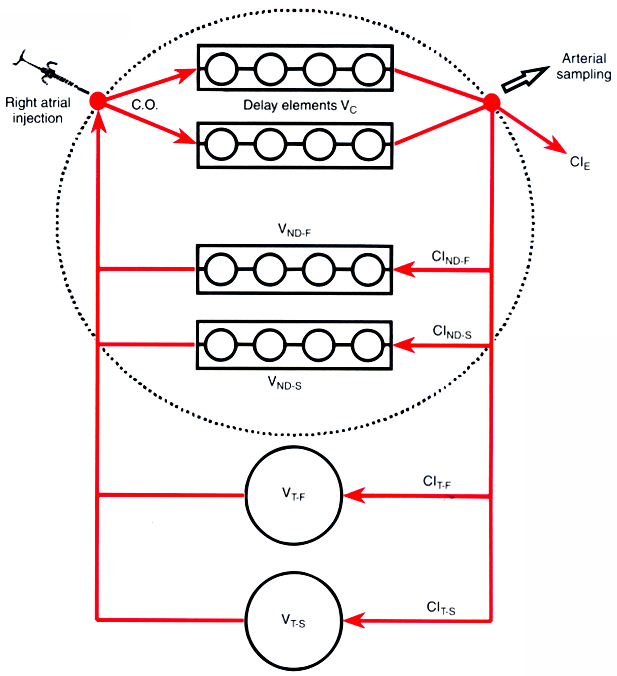
Figure 3-2
A recirculatory model accounting for cardiac output (C.O.),
transit delays and pulmonary uptake (Delay elements VC
), and nondistributive
mixing pathways (VND
and CIND
). All components within the
dashed circle are required to accurately model the
central volume of distribution. In most situations, this complexity is not required,
and the simpler approach of assuming instantaneous mixing within the central volume
is an adequate approximation. CIND-F
and CIND-S
, fast and
slow nondistributive clearances; CIT-F
and CIT-S
, fast and
slow tissue clearances; VND-F
and VND-S
, fast and slow nondistributive
volumes; VT-F
and VT-S
, fast and slow tissue volumes. (From
Krejcie TC, Avram MJ, Gentry WB, et al: A recirculatory model of the pulmonary uptake
and pharmacokinetics of lidocaine based on analysis of arterial and mixed venous
data from dogs. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 25:169–190, 1997.)