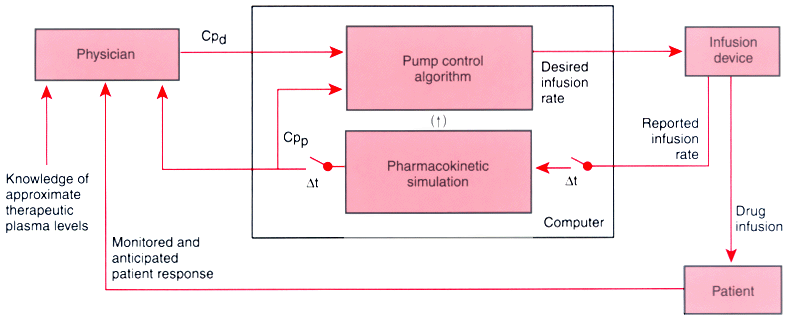
Figure 12-24
Schematic illustration of pharmacokinetic model-driven
drug delivery. The physician enters the target plasma or biophase drug concentration
(Cpd
). An infusion device control algorithm uses a pharmacokinetic model
for the drug being infused to determine what the infusion rate should be for the
next infusion interval (e.g., 9 to 15 seconds). The infusion device delivers drug
to the patient, and the infusion rate is fed into a simulation of the pharmacokinetic
model to compute the current predicted plasma drug concentration (Cpp
).
The variables computed in the simulation are available to the infusion algorithm,
which then calculates the infusion rate necessary for the next 9 to 15 seconds to
achieve the target concentration. On the basis of monitored and anticipated patient
response, knowledge of approximate therapeutic plasma drug concentrations (e.g.,
Cp50
), and Cpp
, the physician can titrate Cpd
as
necessary.