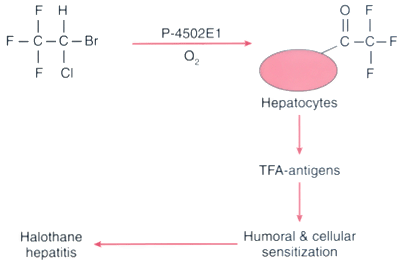
Figure 8-12
Pathway for the generation of the immune response after
anesthetic exposure in susceptible patients. Halothane is metabolized to a trifluoroacetylated
adduct that binds to liver proteins. The altered protein is seen as nonself, generating
an immune response, which on subsequent exposure leads to toxicity and cell death.
A similar process may occur after anesthetic exposure to other fluorinated drugs
that generate a trifluoroacetylated or similar adduct. TFA, trifluoroacetyl (TFA-CI).
(Adapted from Njoku D, Laster MJ, Gong DH, et al: Biotransformation of
halothane, enflurane, isoflurane and desflurane to trifluoroacetylated liver proteins:
Association between protein acylation and liver injury. Anesth Analg 84:173–178,
1997.