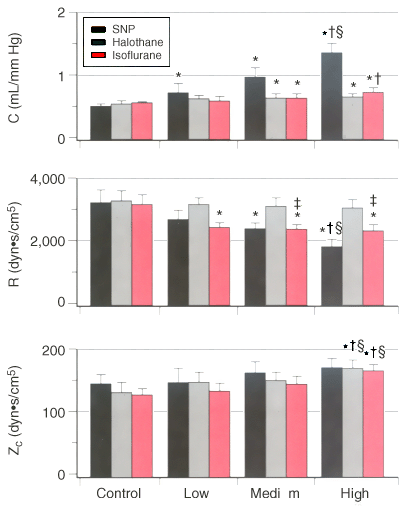
Figure 7-11
Histograms depict the effects of sodium nitroprusside
(SNP), halothane, and isoflurane on total arterial compliance (C, top),
total arterial resistance (R, middle), and characteristic
aortic impedance (ZC
, bottom). The low,
medium, and high doses of volatile anesthetics are 1.25, 1.5, and 1.75 minimum alveolar
concentrations (MACs), respectively. SNP doses produce comparable changes in mean
arterial pressure. *, Significantly (P <
.05) different from the control; †, significantly (P
< .05) different from the low dose; §, significantly (P
< .05) different from the middle dose; ‡, significantly (P
< .05) different from halothane. (Adapted from Hettrick DA, Pagel PS,
Warltier DC: Differential effects of isoflurane and halothane on aortic input impedance
quantified using a three-element Windkessel model. Anesthesiology 83:361–373,
1995.)