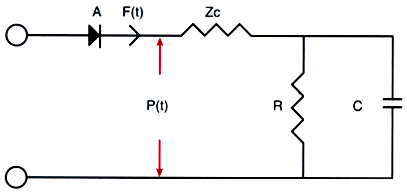
Figure 7-10
Schematic diagram depicting the three-element Windkessel
model of the arterial circulation. Diode A represents the aortic valve. Time-dependent
blood flow [F(t)] and blood pressure [P(t)] entering the arterial system first encounters
the resistance of the ascending aorta (characteristic aortic impedance [Zc]). Further
flow is dictated by total arterial resistance (R) and total arterial compliance (C),
the energy storage component of the arterial vasculature. (Adapted from
Hettrick DA, Pagel PS, Warltier DC: Differential effects of isoflurane and halothane
on aortic input impedance quantified using a three-element Windkessel model. Anesthesiology
83:361–373, 1995.)