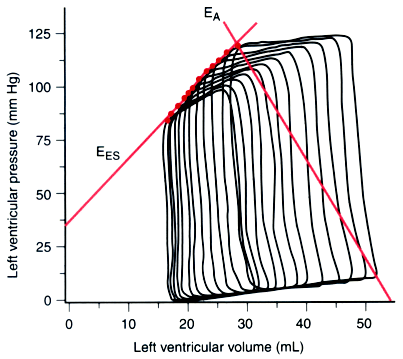
Figure 7-8
Left ventricular (LV) pressure versus LV volume diagrams
during inferior vena caval occlusion and the definition of LV-arterial coupling.
The LV maximal elastances of each pressure-volume diagram are used to calculate
the slope (EES
) of the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship. Effective
arterial elastance (EA
) is determined as the ratio of end-systolic arterial
pressure and stoke volume during steady-state hemodynamic conditions. In the pressure-volume
plane, EA
represents the magnitude of the slope connecting end-systole
to end-diastole. (Adapted from Hettrick DA, Pagel PS, Warltier DC: Desflurane,
sevoflurane, and isoflurane impair canine left ventricular-arterial coupling and
mechanical efficiency. Anesthesiology 85:403–413, 1996.)