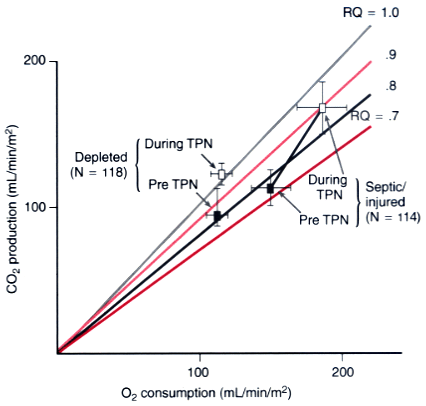
Figure 77-20
Alterations in gas exchange caused by total parenteral
nutrition (TPN) are shown (mean ± SD). Glucose was the primary source of
nonprotein calories, and two responses are seen. Depleted patients show a respiratory
quotient (RQ) above 1.0 with a small increase in V̇O2
,
and hypermetabolic patients have an RQ less than 1.0 with a marked increase in V̇O2
.
Both groups show a large increase in V̇CO2
.
(Adapted from Askanazi J, Carpentier YA, Elwyn DH, et al: Influence of
total parenteral nutrition on fuel utilization in injury and sepsis. Ann Surg 191:40,
1980.)