|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
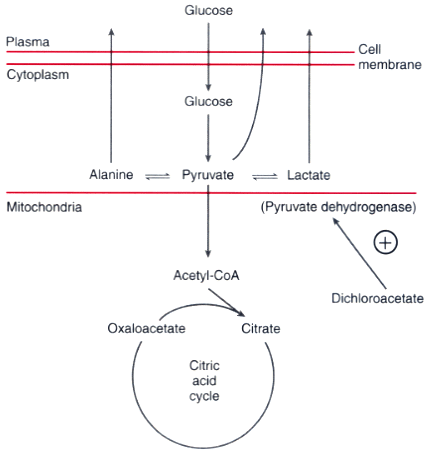
Figure 77-6
Site of action of dichloroacetate (DCA) in mammalian
cells. DCA activates pyruvate dehydrogenase, thereby increasing the flux of C3 compounds
into the tricarboxylic acid cycle and decreasing the release of lactate, pyruvate,
and alanine into the circulation. (Adapted from Blackshear PJ, Fang LST,
Axelrod L: Treatment of severe lactic acidosis with dichloroacetate. Diabetes Care
5:391, 1982.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|