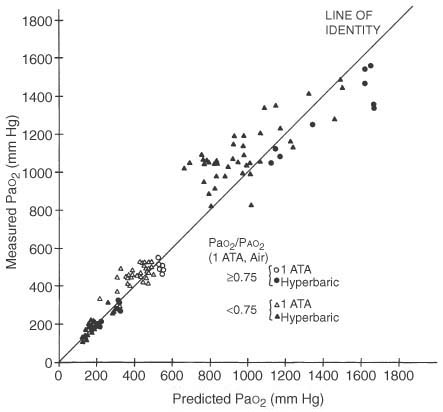
Figure 70-11
Measured versus predicted PaO2
at increased ambient pressure. Predicted PaO2
is calculated from room-air arterial blood gases, assuming that the arterial-alveolar
PO2
ratio (PaO2
/PAO2
,
or a/A ratio) is a constant. Data are shown both
for persons with normal lungs (a/A ratio ≥0.75)
and for patients with gas exchange abnormalities (a/A
ratio <0.75). It is evident that PaO2
predicted in this way is close to the actual measured PaO2
.
(From Moon RE, Camporesi EM, Shelton DL: Prediction of arterial PO2
during hyperbaric treatment. In Bove AA, Bachrach
AJ, Greenbaum LJ Jr [eds]: Underwater and Hyperbaric Physiology IX. Proceedings
of the Ninth International Symposium on Underwater and Hyperbaric Physiology. Bethesda,
MD, Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, 1987, p 1127.)