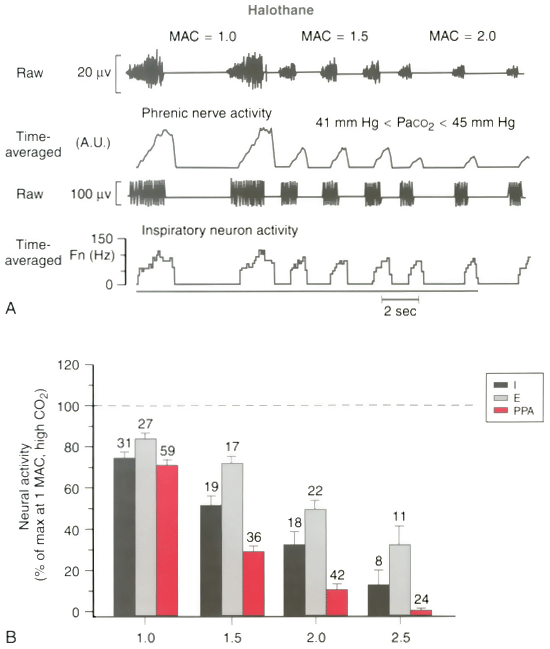
Figure 6-19
Effect of increasing halothane on phrenic nerve and neuron
activity. With increasing anesthetic depth, both peak phrenic nerve (PPA) and peak
neuron activities are depressed. PPA shows the greatest sensitivity to halothane.
A, Phrenic nerve activity and the discharge frequency
of an inspiratory bulbospinal neuron. Inspiratory (phrenic burst) duration decreases
with increasing anesthetic depth. B, Peak expiratory
neuron (E), peak inspiratory neuron (I) activity, and PPA. Expiratory neuronal activity
was most resistant to the effects of halothane. Bars
show the normalized mean ± SEM, and the numbers above the bars indicate the
numbers of neurons studied for each condition. (Adapted from Stuth EAE,
Tonkovic-Capin M, Kampine JP, et al: Dose-dependent effects of halothane on expiratory
and inspiratory bulbospinal neurons and the phrenic nerve activities in dogs. Anesthesiology
81:1470, 1994.)