 |
 |
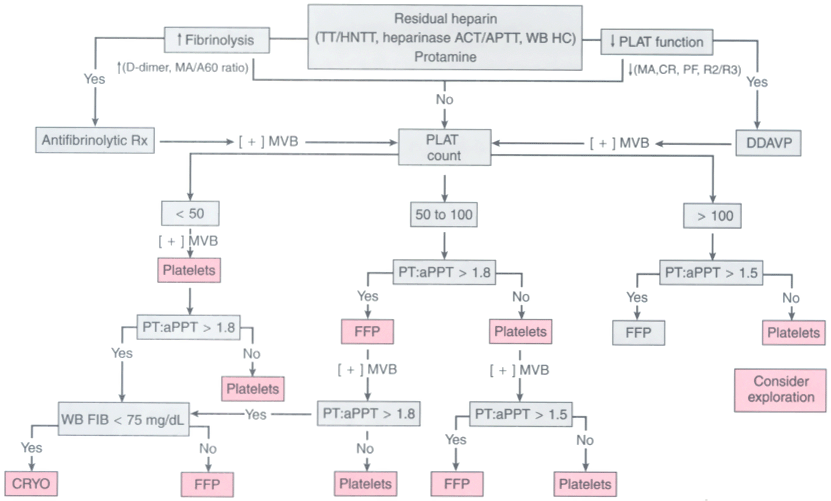
Figure 50-43
Suggested treatment algorithm for patients with excessive
post-cardiopulmonary bypass microvascular bleeding (MVB). Antifibrinolytic Rx, antifibrinolytic
therapy (e.g., epsilon-aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid, aprotinin); CR, clot ratio
values (hemoSTATUS cartridge, Hepcon instrument); DDAVP, desmopressin acetate; D-dimers,
whole blood D-dimer assay (SimpleRED test); FFP, plasma therapy (2 U of fresh frozen
plasma); heparinase ACT, heparinase kaolin-activated clotting time test (ACT instrument);
heparinase aPTT, heparinase, activated partial thromboplastin time test (Coagucheck
Plus); MA, maximum amplitude (thromboelastograph); MA/A60
ratio, maximum
amplitude/amplitude at 60 minutes (thromboelastograph); [+] MVB, continued microvascular
bleeding; PF, platelet force measurements (Hemodyne Instrument); PLAT count, platelet
count (1000/µL); Platelets, platelet transfusion (6 U of random donor or apheresis
unit equivalent); PT:aPTT, prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin
time control values (values/mean values from a normal reference population); R2/R3,
R2 and R3 slope values (Sonoclot instrument); TT/HNTT, whole blood thrombin time/heparin-neutralized
thrombin time test (Hemochron instrument); WB FIB, whole blood fibrinogen test (Hemochron
instrument); WB HC, whole blood heparin concentration cartridge (Hepcon instrument).
(Redrawn from Despotis GJ, Joist JH, Goodnough LT: Monitoring hemostasis
with cardiac surgery: The impact of point-of-care testing on blood loss and transfusion
outcomes. Clin Chem 43:1684–1969, 1997.)
 |
