ST Segment and T Wave
Repolarization of the ventricles begins at the end of the QRS
complex and consists of the ST segment and T wave. Whereas ventricular depolarization
occurs along established conduction pathways, ventricular repolarization is a prolonged
process that occurs independently in every cell. The T wave represents the uncancelled
potential differences of ventricular repolarization. The junction of the QRS and
the ST segment is the J junction. The T wave is sometimes followed by a small U
wave, the origin of which is unclear. An inverted U wave has been associated with
several clinically significant conditions, such as hypertension, coronary artery
disease, valvular heart disease, and certain metabolic disorders. There may be an
association between exercise- or rest-related U-wave
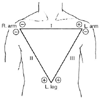 Figure 34-2
Einthoven triangle. (From Thys DM, Kaplan JA:
The ECG in Anesthesia and Critical Care. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1987.)
Figure 34-2
Einthoven triangle. (From Thys DM, Kaplan JA:
The ECG in Anesthesia and Critical Care. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1987.)
inversion and significant stenosis of the left anterior descending artery or the
left main coronary artery.
 Figure 34-2
Einthoven triangle. (From Thys DM, Kaplan JA:
The ECG in Anesthesia and Critical Care. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1987.)
Figure 34-2
Einthoven triangle. (From Thys DM, Kaplan JA:
The ECG in Anesthesia and Critical Care. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1987.)