Physicochemical Characteristics
Propofol ( Fig.
10-1
) is one of a group of alkylphenols that have hypnotic properties in
animals.[5]
The alkylphenols are oils at room temperature
and insoluble in aqueous solution, but they are highly lipid soluble. Today, several
formulations are presently marketed, and several others are in development. The
formulation that followed the removal of Cremophor consists of 1% (weight/volume)
propofol, 10% soybean oil, 2.25% glycerol, and 1.2% purified egg phosphatide. Because
of concern regarding microbial growth in the emulsion, disodium edetate (0.005%)
was added as a retardant of bacterial growth. This formulation has a pH of 7 and
appears as a slightly viscous, milky white substance. A second formulation
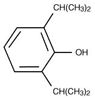 Figure 10-1
Structure of propofol, an alkylphenol derivative.
Figure 10-1
Structure of propofol, an alkylphenol derivative.
containing metabisulfite as the antimicrobial has also been introduced for commercial
use in the United States. In Europe, a 2% formulation is also available, as well
as a formulation in which the emulsion contains a mixture of medium- and long-chain
triglycerides. All formulations available commercially are stable at room temperature
and are not light sensitive. Changes in the diluent may result in slight changes
in pharmacokinetics, cracking of the emulsion, spontaneous degradation of propofol,
and possibly changes in pharmacologic effect. If a dilute solution of propofol is
required, it is compatible with 5% dextrose in water.
 Figure 10-1
Structure of propofol, an alkylphenol derivative.
Figure 10-1
Structure of propofol, an alkylphenol derivative.