Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
All patients are evaluated preoperatively by TEE to exclude the
possibility of persistent left SVC or patent foramen ovale. Table
66-3
lists the major exclusion criteria for robotic coronary artery bypass
grafting. The iliac and femoral arteries should also be evaluated for their size
by echo Doppler ultrasonography.[30]
Patients are prepared and monitored for anesthesia in a manner
similar to that for mitral valve surgery (see "Mitral Valve Repair"). Monitoring
of the right radial artery pressure tracing is imperative when using an endovascular
balloon-occlusion catheter. After the patient is asleep, inspired oxygen tension
and expired carbon dioxide are monitored. TEE is used routinely as the standard
of care for determination of cardiac function and for
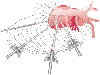 Figure 66-8
Incision ports for coronary artery bypass grafting.
Trocars are placed in the third, sixth, and eighth intercostal spaces. Similar port
positions are used for bilateral internal mammary artery dissection.
Figure 66-8
Incision ports for coronary artery bypass grafting.
Trocars are placed in the third, sixth, and eighth intercostal spaces. Similar port
positions are used for bilateral internal mammary artery dissection.
confirming catheter placement. Pulmonary artery catheters are judiciously used in
the appropriate patient population, but the data that the catheter provide may be
redundant when TEE data are available. The patient is positioned the same as for
internal mammary artery takedown, and trocar positions are placed as depicted in
Figure 66-8
.
When cardiopulmonary bypass is anticipated, the left femoral artery
is cannulated with a 17- or 21-Fr Remote Access Perfusion (RAP) catheter ( Fig.
66-9
) with an aortic occlusion balloon. Exclusion criteria for endovascular
cardiopulmonary bypass are contained in Table
66-4
. This catheter allows anterograde flow of 4 or 5 L/min, respectively.
The cannula has a separate lumen for delivering cardioplegia to the aortic root
beyond the occlusion of the balloon. The aortic cannula is positioned in the ascending
aorta, 2 cm above the aortic valve, with TEE guidance ( Fig.
66-10
). The endovascular balloon is inflated with a volume equal to the
diameter (in milliliters) of the sinotubular junction of the aorta. A balloon pressure
above 300 mm Hg usually provides complete occlusion of the aorta.[32]
Residual flow around the balloon can be seen and monitored with color flow on TEE.
The use of bilateral radial artery lines is useful in detecting the migration of
the occlusion balloon toward the innominate artery. Proximal migration of the balloon
can most easily be seen with TEE, preventing balloon herniation through the aortic
valve.
After full cannulation and being poised for cardiopulmonary bypass,
the right lung is allowed to collapse, and left lung ventilation is begun. The ventilator
is adjusted to provide an end-tidal carbon dioxide pressure of 35 to 40 mm Hg. Ports
can be safely placed after the right-sided pneumothorax has formed. Carbon dioxide
is insufflated
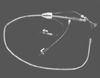 Figure 66-9
Remote Access Perfusion (RAP) catheter (Estech Systems,
Inc., Plano, TX). The endovascular catheter has a cylindrical balloon for endovascular
aortic clamping. The catheter provides anterograde perfusion of the aortic arch
at a rate of 5 L/min and cardioplegia administration to the aortic root.
Figure 66-9
Remote Access Perfusion (RAP) catheter (Estech Systems,
Inc., Plano, TX). The endovascular catheter has a cylindrical balloon for endovascular
aortic clamping. The catheter provides anterograde perfusion of the aortic arch
at a rate of 5 L/min and cardioplegia administration to the aortic root.
into the right hemithorax and continued at a pressure of 5 to 10 mm Hg. This allows
the affected lung to collapse further and provides a larger visual field. It may
also prevent mediastinal shifts during one-lung ventilation when large tidal volumes
are used, such as in a patient with emphysematous lungs. Insufflation to produce
a deliberate pneumothorax is not very effective at raising the sternum above the
anterior surface of the heart. For this reason, some surgeons provide sternal lift
retractors to increase the retrosternal space and provide better exposure.[52]
Robot-assisted, beating-heart coronary artery bypass grafting
can be accomplished with appropriate patient selection. Articulating stabilizers
passed through a subxiphoid port can stabilize the anterior surface of the heart
to facilitate grafting.[53]
Bilateral internal
mammary artery grafting has also been accomplished.[54]
 Figure 66-8
Incision ports for coronary artery bypass grafting.
Trocars are placed in the third, sixth, and eighth intercostal spaces. Similar port
positions are used for bilateral internal mammary artery dissection.
Figure 66-8
Incision ports for coronary artery bypass grafting.
Trocars are placed in the third, sixth, and eighth intercostal spaces. Similar port
positions are used for bilateral internal mammary artery dissection. Figure 66-9
Remote Access Perfusion (RAP) catheter (Estech Systems,
Inc., Plano, TX). The endovascular catheter has a cylindrical balloon for endovascular
aortic clamping. The catheter provides anterograde perfusion of the aortic arch
at a rate of 5 L/min and cardioplegia administration to the aortic root.
Figure 66-9
Remote Access Perfusion (RAP) catheter (Estech Systems,
Inc., Plano, TX). The endovascular catheter has a cylindrical balloon for endovascular
aortic clamping. The catheter provides anterograde perfusion of the aortic arch
at a rate of 5 L/min and cardioplegia administration to the aortic root.