Psychoprophylaxis
"Natural childbirth" stems from a phrase coined by Grantley Dick-Read
in 1933; he believed that childbirth was a painless process that did not need medical
intervention if the mother was adequately prepared.[65]
The Pavlovian methods of childbirth used in Russia were adapted by the French obstetrician
Fernand Lamaze in the late 1950s, and "natural childbirth" was popularized as an
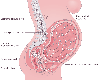 Figure 58-6
Pathways of labor pain illustrating the nerve pathways
responsible for pain in the various stages of labor and the types of blocks that
can block nerve impulse transmission through these pathways to alleviate labor pain.
(Redrawn from Eltzchig HK, Lieberman ES, Camann WR: Regional anesthesia
and analgesia for labor and delivery. N Engl J Med 348:319, 2003.)
Figure 58-6
Pathways of labor pain illustrating the nerve pathways
responsible for pain in the various stages of labor and the types of blocks that
can block nerve impulse transmission through these pathways to alleviate labor pain.
(Redrawn from Eltzchig HK, Lieberman ES, Camann WR: Regional anesthesia
and analgesia for labor and delivery. N Engl J Med 348:319, 2003.)
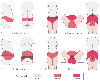 Figure 58-7
Distribution and intensity of labor pain during each
stage of labor and delivery. In the early first stage (A),
pain is referred to the T11 and T12 dermatomes. During the late first stage (B),
pain also extends to the T10 and L1 dermatomes. In the second stage (C),
in addition to the dermatomal distribution of late first stage, pain is also felt
as pressure in the lower part of the back and perineum and the upper part of the
legs. During the end of the second stage and for delivery (D),
pain originates from the perineum. (Redrawn from Bonica JJ: Obstetric Analgesia
and Anesthesia. World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Seattle, University
of Washington Press. As modified by Bonica JJ: The nature of pain in parturition.
In Van Zundert A, Ostheimer GW [eds]: Pain Relief
and Anesthesia in Obstetrics. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1996, p 32.)
Figure 58-7
Distribution and intensity of labor pain during each
stage of labor and delivery. In the early first stage (A),
pain is referred to the T11 and T12 dermatomes. During the late first stage (B),
pain also extends to the T10 and L1 dermatomes. In the second stage (C),
in addition to the dermatomal distribution of late first stage, pain is also felt
as pressure in the lower part of the back and perineum and the upper part of the
legs. During the end of the second stage and for delivery (D),
pain originates from the perineum. (Redrawn from Bonica JJ: Obstetric Analgesia
and Anesthesia. World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Seattle, University
of Washington Press. As modified by Bonica JJ: The nature of pain in parturition.
In Van Zundert A, Ostheimer GW [eds]: Pain Relief
and Anesthesia in Obstetrics. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1996, p 32.)
option for parturtients. This method focuses on teaching the mother conditioned
reflexes to overcome the pain and fear of childbirth. It also uses an education
program, human support during labor, breathing techniques, relaxation techniques
of voluntary muscles, a strong focus of attention, and specific activities to concentrate
on during contractions to block pain. Indeed, even the effect of the presence of
another woman during labor to support the expectant mother has been shown to have
a positive effect on outcomes, including the duration of labor.[66]
 Figure 58-6
Pathways of labor pain illustrating the nerve pathways
responsible for pain in the various stages of labor and the types of blocks that
can block nerve impulse transmission through these pathways to alleviate labor pain.
(Redrawn from Eltzchig HK, Lieberman ES, Camann WR: Regional anesthesia
and analgesia for labor and delivery. N Engl J Med 348:319, 2003.)
Figure 58-6
Pathways of labor pain illustrating the nerve pathways
responsible for pain in the various stages of labor and the types of blocks that
can block nerve impulse transmission through these pathways to alleviate labor pain.
(Redrawn from Eltzchig HK, Lieberman ES, Camann WR: Regional anesthesia
and analgesia for labor and delivery. N Engl J Med 348:319, 2003.) Figure 58-7
Distribution and intensity of labor pain during each
stage of labor and delivery. In the early first stage (A),
pain is referred to the T11 and T12 dermatomes. During the late first stage (B),
pain also extends to the T10 and L1 dermatomes. In the second stage (C),
in addition to the dermatomal distribution of late first stage, pain is also felt
as pressure in the lower part of the back and perineum and the upper part of the
legs. During the end of the second stage and for delivery (D),
pain originates from the perineum. (Redrawn from Bonica JJ: Obstetric Analgesia
and Anesthesia. World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Seattle, University
of Washington Press. As modified by Bonica JJ: The nature of pain in parturition.
In Van Zundert A, Ostheimer GW [eds]: Pain Relief
and Anesthesia in Obstetrics. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1996, p 32.)
Figure 58-7
Distribution and intensity of labor pain during each
stage of labor and delivery. In the early first stage (A),
pain is referred to the T11 and T12 dermatomes. During the late first stage (B),
pain also extends to the T10 and L1 dermatomes. In the second stage (C),
in addition to the dermatomal distribution of late first stage, pain is also felt
as pressure in the lower part of the back and perineum and the upper part of the
legs. During the end of the second stage and for delivery (D),
pain originates from the perineum. (Redrawn from Bonica JJ: Obstetric Analgesia
and Anesthesia. World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Seattle, University
of Washington Press. As modified by Bonica JJ: The nature of pain in parturition.
In Van Zundert A, Ostheimer GW [eds]: Pain Relief
and Anesthesia in Obstetrics. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1996, p 32.)