USE OF NERVE STIMULATORS WITHOUT RECORDING EQUIPMENT
Although it is my opinion that neuromuscular function should be
monitored objectively whenever a neuromuscular blocking drug is administered to a
patient, tactile or visual evaluation of the evoked response is still the most common
form of clinical neuromuscular monitoring. The following is a description of how
this is best done.
First, for supramaximal stimulation, careful cleansing of the
skin and proper placement and fixation of electrodes are essential. Second, every
effort should be taken
 Figure 39-18
Predicted probabilities of postoperative pulmonary complications
in different age groups in orthopedic, gynecologic, and major abdominal surgery with
a duration of anesthesia of less than 200 minutes. The solid lines represent patients
having residual neuromuscular block (TOF < 0.70) following the use of pancuronium;
the broken lines represent patients with TOF ≥ 0.70 following the use of pancuronium
as well as all patients following the use of atracurium and vecuronium, independent
of the TOF ratio at the end of anesthesia.[99]
Figure 39-18
Predicted probabilities of postoperative pulmonary complications
in different age groups in orthopedic, gynecologic, and major abdominal surgery with
a duration of anesthesia of less than 200 minutes. The solid lines represent patients
having residual neuromuscular block (TOF < 0.70) following the use of pancuronium;
the broken lines represent patients with TOF ≥ 0.70 following the use of pancuronium
as well as all patients following the use of atracurium and vecuronium, independent
of the TOF ratio at the end of anesthesia.[99]
to prevent central cooling as well as cooling of the extremity being evaluated.
Both central and local surface cooling of the adductor pollicis muscle may reduce
the twitch tension and the TOF ratio.[105]
[106]
Peripheral cooling may affect nerve conduction, decrease the rate of release of
acetylcholine and muscle contractility, increase skin impedance, and reduce blood
flow to the muscles, thus decreasing the rate of removal of muscle relaxant from
the neuromuscular junction. These factors may account for the occasional very pronounced
difference in muscle response between a cold extremity and the contralateral warm
extremity.[107]
Third, when possible, the response
to
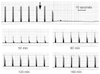 Figure 39-19
Typical recording of the mechanical response (Myograph
2000) to TOF nerve stimulation of the ulnar nerve after injection of 1 mg/kg of succinylcholine
(arrow) in a patient with genetically determined
abnormal plasma cholinesterase activity. The prolonged duration of action and the
pronounced fade in the response indicate a phase II block.
Figure 39-19
Typical recording of the mechanical response (Myograph
2000) to TOF nerve stimulation of the ulnar nerve after injection of 1 mg/kg of succinylcholine
(arrow) in a patient with genetically determined
abnormal plasma cholinesterase activity. The prolonged duration of action and the
pronounced fade in the response indicate a phase II block.
nerve stimulation should be evaluated by feel and not by eye, and the response of
the thumb (rather than that of the fifth finger) should be evaluated. Direct stimulation
of the muscle often causes subtle movements of the fifth finger when no response
is present at the thumb. Finally, the different sensitivities of various muscle
groups to neuromuscular blocking agents should always be kept in mind.
Figure 39-20
shows which modes of nerve stimulation can be used at various periperative times.
Use of a Peripheral Nerve Stimulator During Induction
of Anesthesia
The nerve stimulator should be attached to the patient before
induction of anesthesia but should not be turned on until after the patient is unconscious.
Single-twitch stimulation at 1 Hz may be used initially when seeking supramaximal
stimulation. However, after supramaximal stimulation has been ensured and before
muscle relaxant is injected, the mode of stimulation should be changed to TOF (or
0.1-Hz twitch stimulation). Then, after the response to this stimulation has been
observed (the control response), the neuromuscular blocking agent is injected. Although
the trachea is often intubated when the response to TOF stimulation disappears, postponement
of this procedure for 30 to 90 seconds, depending upon the muscle relaxant used,
usually produces better conditions.
 Figure 39-18
Predicted probabilities of postoperative pulmonary complications
in different age groups in orthopedic, gynecologic, and major abdominal surgery with
a duration of anesthesia of less than 200 minutes. The solid lines represent patients
having residual neuromuscular block (TOF < 0.70) following the use of pancuronium;
the broken lines represent patients with TOF ≥ 0.70 following the use of pancuronium
as well as all patients following the use of atracurium and vecuronium, independent
of the TOF ratio at the end of anesthesia.[99]
Figure 39-18
Predicted probabilities of postoperative pulmonary complications
in different age groups in orthopedic, gynecologic, and major abdominal surgery with
a duration of anesthesia of less than 200 minutes. The solid lines represent patients
having residual neuromuscular block (TOF < 0.70) following the use of pancuronium;
the broken lines represent patients with TOF ≥ 0.70 following the use of pancuronium
as well as all patients following the use of atracurium and vecuronium, independent
of the TOF ratio at the end of anesthesia.[99]
 Figure 39-19
Typical recording of the mechanical response (Myograph
2000) to TOF nerve stimulation of the ulnar nerve after injection of 1 mg/kg of succinylcholine
(arrow) in a patient with genetically determined
abnormal plasma cholinesterase activity. The prolonged duration of action and the
pronounced fade in the response indicate a phase II block.
Figure 39-19
Typical recording of the mechanical response (Myograph
2000) to TOF nerve stimulation of the ulnar nerve after injection of 1 mg/kg of succinylcholine
(arrow) in a patient with genetically determined
abnormal plasma cholinesterase activity. The prolonged duration of action and the
pronounced fade in the response indicate a phase II block.