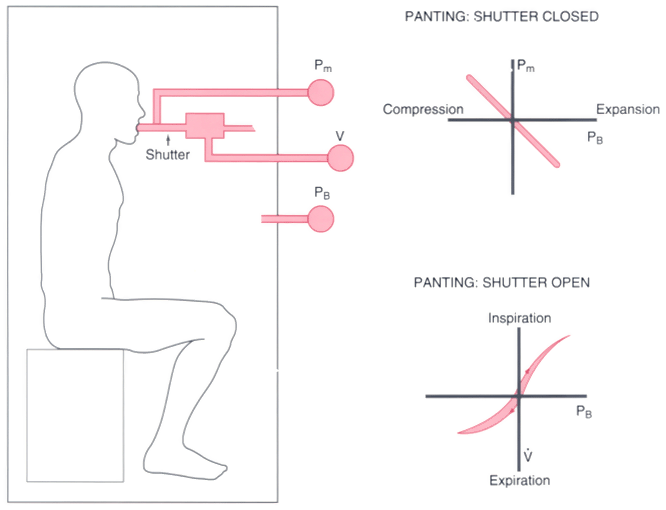
Figure 26-10
Diagram of the constant-volume body plethysmograph used
to measure airway resistance and lung volume. When a subject pants against an obstructed
mouthpiece (shutter closed), box pressure (PB
) is plotted against mouth
pressure (Pm
). Changes in PB
are converted to changes in lung
volume by calibration of the box with known volumes of added gas and observation
of PB
changes. As the subject pants through the open mouthpiece, flow
(V) replaces Pm
on the plot, and airway resistance is computed from the
relationship between PB
and V.