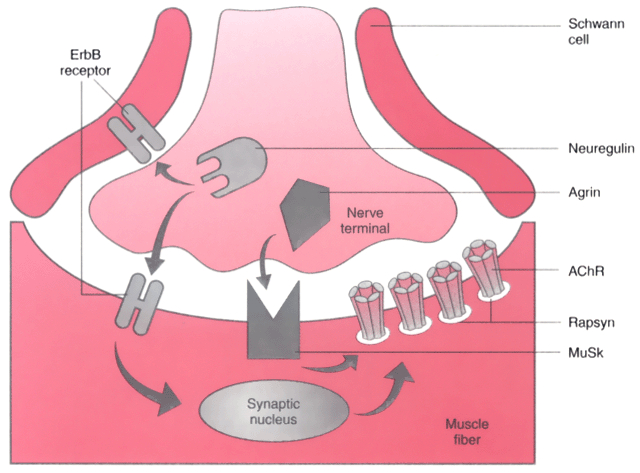
Figure 22-5
Diagram of agrin- and ARIA/neuregulin-dependent events
during neuromuscular junction maturation. After establishment of a nerve on the
muscle, growth factors, including agrin and ARIA (acetylcholine receptor-inducing
activity), are released. Agrin interacting with its receptor MuSK (muscle-specific
kinase) enhances the clustering of the synaptic proteins, including acetylcholine
receptors (AChRs), rapsyn, and ERBB receptors. ARIA is the best candidate for involvement
in the conversion of γ-subunit-containing immature receptor to epsilon-subunit-containing
mature (innervated) receptor, which is synapse specific and therefore not inserted
in the extrajunctional area.