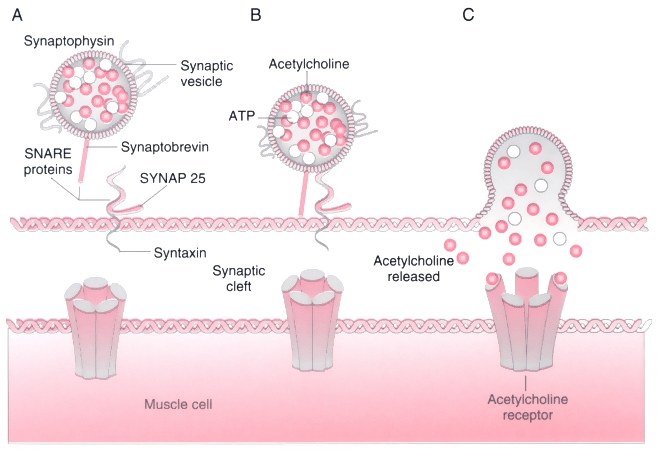
Figure 22-3
Model for protein-mediated membrane fusion and exocytosis.
A, The release of acetylcholine from the vesicles
is mediated by a series of proteins collectively called SNARE proteins. Synaptotagmin
is the neuronal Ca2+
receptor detecting Ca2+
entry. Synaptobrevin
(i.e., vesicle-associated membrane protein [VAMP]) is a filament-like protein on
the vesicle. B, During depolarization and calcium
entry, synaptobrevin on the vesicle unfolds and forms a ternary complex with syntaxin/SNAP-25.
This process is facilitated by phosphorylation of synapsin, also present on the
vesicle membrane. C, Assembly of the ternary complex
forces the vesicle in close apposition to the nerve membrane at the active zone with
release of its contents, acetylcholine. The fusion is disassembled, and the vesicle
is recycled.