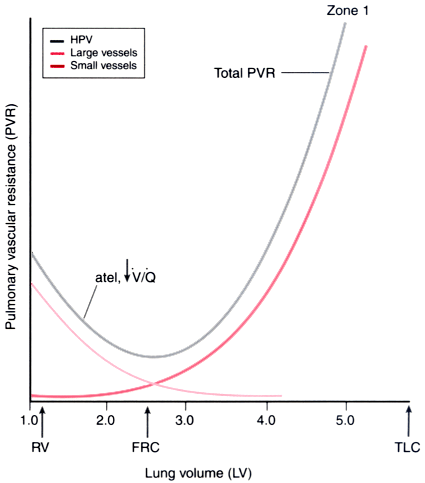
Figure 17-8
Total pulmonary vascular resistance relates to lung volume
as an asymmetric U-shaped curve. The trough of the curve occurs when lung volume
equals functional residual capacity (FRC). Total pulmonary resistance is the sum
of the resistance in small vessels (increased by increasing lung volume) and the
resistance in large vessels (increased by decreasing lung volume). The end point
for increasing lung volume (toward total lung capacity [TLC]) is the creation of
zone 1 conditions, and the end point for decreasing lung volume (toward residual
volume [RV]) is the creation of low ventilation-perfusion (V̇A/ )
and atelectatic (atel) areas that demonstrate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
(HPV). The curve represents a composite of data from references [20]
[21]
and [23]
.
)
and atelectatic (atel) areas that demonstrate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
(HPV). The curve represents a composite of data from references [20]
[21]
and [23]
.
![]() )
and atelectatic (atel) areas that demonstrate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
(HPV). The curve represents a composite of data from references [20]
[21]
and [23]
.
)
and atelectatic (atel) areas that demonstrate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
(HPV). The curve represents a composite of data from references [20]
[21]
and [23]
.