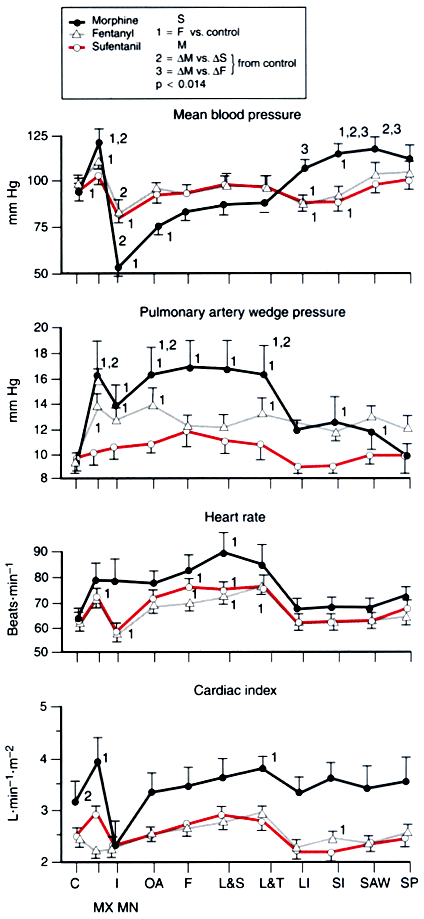
Figure 11-28
Hemodynamic changes during cardiac surgery in patients
administered with morphine, fentanyl, or sufentanil. Total doses were 4.4 mg/kg,
95.4 µg/kg and 18.9 µg/kg for morphine, fentanyl and sufentanil, respectively.
Cardiovascular variables were analyzed before induction (C), and at the time of
maximal (MX) and minimal (MN) systolic arterial pressure change after induction (I),
insertion of oral airway (OA), insertion of Foley catheter (F), laryngoscopy + endotracheal
lidocaine spray (L&S), laryngoscopy + endotracheal intubation (L&T), leg
incision (LI), sternal incision (SI), sternal saw (SAW), and sternal spread (SP).
(From Benthuysen JL, Foltz BD, Smith NT, et al: Prebypass hemodynamic stability
of sufentanil-O2
, fentanyl-O2
, and morphine-O2
anesthesia
during cardiac surgery: A comparison of cardiovascular profiles. J Cardiothorac
Anesth 12:749–757, 1988.)