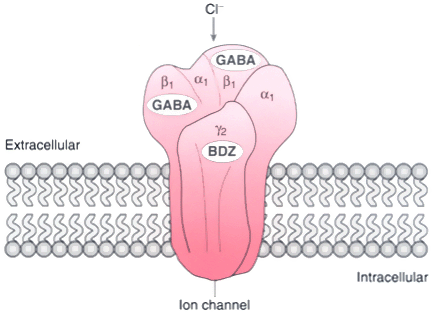
Figure 10-14
Model of the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-benzodiazepine
receptor complex. Current data suggest a pentameric protein composed of α-,
β-, and γ-subunits; the proposed arrangement of subunits is arbitrary.
There are two sites for GABA binding (on the β-subunits) and a single site
for benzodiazepine (BDZ) binding (depicted on the γ2
-subunit).
Homology between the GABAα
receptor and the nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor suggests that the chloride ion channel is formed by contributions from each
subunit. (Redrawn with modification from Zorumski CF, Isenberg KE: Insights
into the structure and function of GABA-benzodiazepine receptors: Ion channels and
psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry 148:162, 1991.)