|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
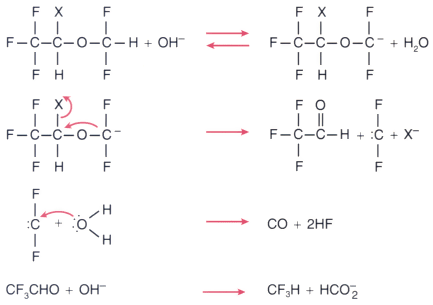
Figure 8-21
Proposed mechanism of carbon monoxide formation from
difluoromethyl-ethyl ether anesthetics. The backbone structures for isoflurane (X
= CI) and desflurane (X = F) are shown, along with a putative mechanism for the concomitant
formation of trifluoromethane. Water in line 3 may also react as OH-
(Adapted from Baxter PJ, Garton K, Kharasch ED: Mechanistic aspects of
carbon monoxide formation from volatile anesthetics. Anesthesiology 89:929–941,
1998.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|