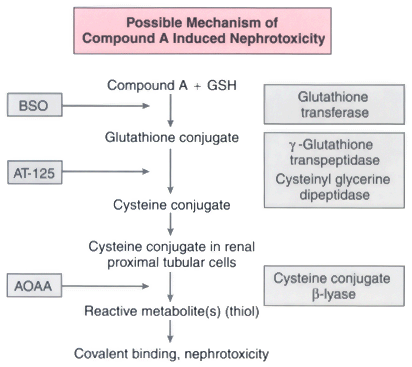
Figure 8-19
Crucial steps in the β-lyase pathway: First, conjugation
of compound A with glutathione in the liver is mediated by glutathione S-transferase;
this conjugate is then transported to the kidney. Second, the glutathione S-conjugate
is converted to a cysteine S-conjugate, a process
mediated by γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Third, the cysteine S-conjugate
of compound A is then converted to a reactive thiol, mediated by renal cysteine conjugate
β-lyase; DL-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine
(BSO) depletes endogenous stores of glutathione in the body, acivicin (AT-125) inhibits
the activity of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, and aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA) inhibits
the activity of β-lyase. Compound A, its conjugates, and the reactive thiol
have all been postulated to cause the renal necrosis that can occur in rats after
the administration of compound A and the glucosuria and enzymuria that can result
in rats and humans from compound A administration.