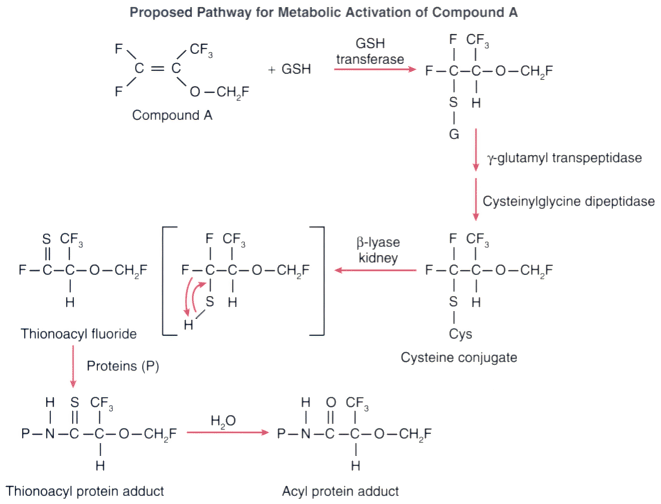
Figure 8-18
Proposed pathway for the metabolic activation of compound
A shows formation of an intrahepatic glutathione (GSH) conjugate of compound A that
is translocated to the kidney, where γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, cysteinylglycine
dipeptidase, and renal cysteine conjugate β-lyase catalyze the formation of
a nephrotoxic thiol, which can acylate kidney proteins. (Adapted from Martin
JL, Kandel L, Laster MJ, et al: Studies of the mechanism of nephrotoxicity of compound
A in rats. J Anesth 11:32–37, 1997.)