 |
 |
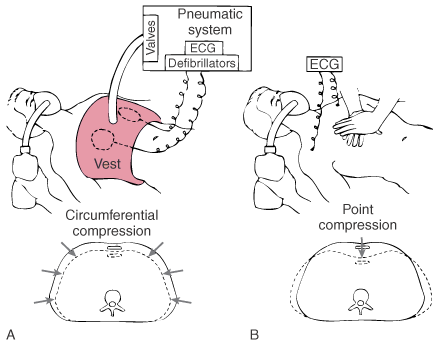
Figure 78-2
Comparison of the thoracic vest system (A)
for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (vest CPR) and standard manual CPR (B).
The vest contains a bladder that is inflated and deflated by a pneumatic system.
The lower panels show schematic representations
of transverse sections of the midthorax during vest CPR and manual CPR. Thoracic
size during chest relaxation is shown by the solid lines.
The arrows indicate force applied to the thorax
during chest compression. Vest inflation produces a relatively uniform decrease
in dimensions of the thorax. With manual CPR, the sternum is displaced during compression
(arrow) and the lateral aspect of the thorax can
bulge, thereby increasing thoracic volume and reducing the intrathoracic pressure
generated during compression. (Redrawn with modification from Halperin HR,
Tsitlik JE, Gelfand M, et al: A preliminary study of cardiopulmonary resuscitation
by circumferential compression of the chest with use of a pneumatic vest. N Engl
J Med 329:762, 1993.)
 |
