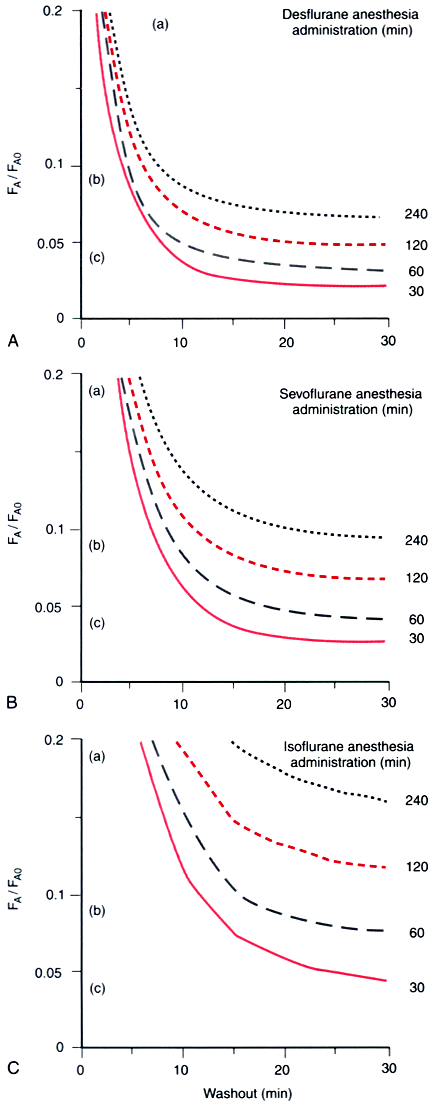
Figure 5-18
Both solubility and duration of anesthesia affect the
fall of the alveolar concentration (FA) from its
value immediately preceding the cessation of anesthetic administration (FA0
).
A longer anesthetic slows the fall, as does a greater solubility, and the effects
are shown for the increasingly soluble desflurane, sevoflurane, and isoflurane (A
to C). The horizontal lines designated (a), (b),
and (c) indicate 80%, 90%, and 95% decreases, respectively, in the alveolar concentration
from the concentration at the end of anesthesia. (Data from Yasuda N, Lockhart
SH, Eger EI II, et al: Kinetics of desflurane, isoflurane, and halothane in humans.
Anesthesiology 74:489–498, 1991, and from Yasuda N, Lockhart SH, Eger EI II,
et al: Comparison of kinetics of sevoflurane and isoflurane in humans. Anesth Analg
72:316–324, 1991.)