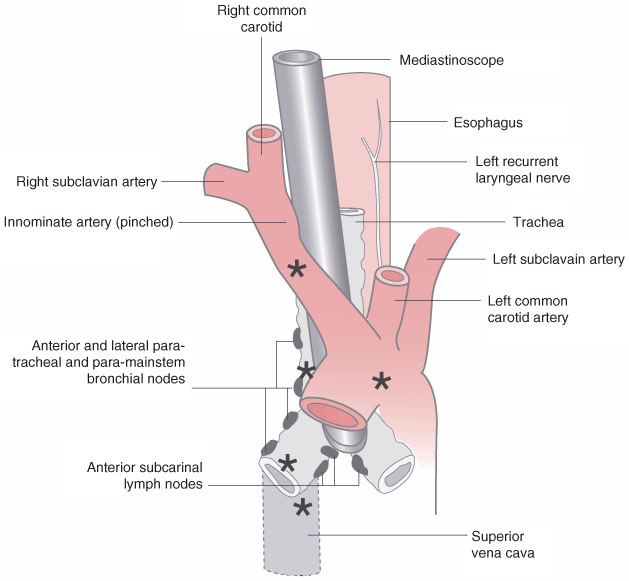
Figure 49-34
Schematic diagram showing placement of a mediastinoscope
into the superior mediastinum. The mediastinoscope passes anterior to the trachea
but behind the thoracic aorta. This location allows for sampling of the anterior
and lateral para-main stem bronchial lymph nodes, anterior subcarinal lymph nodes,
and anterior and lateral paratracheal lymph nodes. Anatomic structures that can
be compressed by the mediastinoscope (see areas marked by asterisks)
and result in major complications are the thoracic aorta (rupture, reflex bradycardia),
innominate artery (decreased right carotid blood flow can cause cerebrovascular symptoms,
and decreased right subclavian flow can cause loss of the right radial pulse), trachea
(inability to ventilate, stimulus to cough), and vena cava (risk of hemorrhage with
superior vena cava syndrome).