Dibucaine Number and Butyrylcholinesterase Activity
Butyrylcholinesterase is synthesized by the liver and is found
in plasma. The neuromuscular block induced by succinylcholine is prolonged by a
decreased concentration or activity of the enzyme. The activity of the enzyme refers
to the number of substrate molecules (µmol) hydrolyzed per unit of time, often
expressed in international units (IU). The normal range of butyrylcholinesterase
activity is quite large, and as demonstrated by Viby-Mogensen,[69]
significant decreases in butyrylcholinesterase activity result in modest increases
in the time required to achieve 100% twitch recovery ( Fig.
13-6
).
Factors that have been found to lower butyrylcholinesterase activity
are liver disease,[74]
advanced age,[75]
malnutrition, pregnancy, burns, oral contraceptives, monoamine oxidase inhibitors,
echothiophate, cytotoxic drugs, neoplastic disease, anticholinesterase drugs,[76]
[77]
tetrahydroaminacrine,[78]
hexafluorenium,[79]
[80]
and metoclopramide.[81]
The histamine type 2 (H2
)
receptor antagonists have no effect on butyrylcholinesterase activity or the duration
of succinylcholine effect.[82]
Bambuterol, a prodrug
of terbutaline, produces marked inhibition of butyrylcholinesterase activity and
causes prolongation of
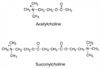 Figure 13-5
Structural relationship of succinylcholine, a depolarizing
neuromuscular blocking agent, to acetylcholine. Succinylcholine consists of two
acetylcholine molecules linked through the acetate methyl groups. Like acetylcholine,
succinylcholine stimulates nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
Figure 13-5
Structural relationship of succinylcholine, a depolarizing
neuromuscular blocking agent, to acetylcholine. Succinylcholine consists of two
acetylcholine molecules linked through the acetate methyl groups. Like acetylcholine,
succinylcholine stimulates nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
succinylcholine-induced blockade.[83]
[84]
The β-blocker esmolol inhibits butyrylcholinesterase but causes only minor
prolongation of succinylcholine blockade.[85]
[86]
Despite all the publications and efforts to identify situations
in which normal butyrylcholinesterase enzyme activity may be low, this has not been
a major concern in clinical practice because even large decreases in butyrylcholinesterase
activity result in only moderate increases in the duration of action of succinylcholine.
When butyrylcholinesterase activity is reduced to 20% of normal by severe liver
disease, the duration of apnea after the administration of succinylcholine increases
from a normal duration of 3 minutes to only 9 minutes. Even when glaucoma treatment
with echothiophate decreased butyrylcholinesterase activity from 49% of control to
no activity, the increase in duration of neuromuscular blockade varied from 2 to
14 minutes. In no patient did the total duration of neuromuscular blockade exceed
23 minutes.[87]
 Figure 13-5
Structural relationship of succinylcholine, a depolarizing
neuromuscular blocking agent, to acetylcholine. Succinylcholine consists of two
acetylcholine molecules linked through the acetate methyl groups. Like acetylcholine,
succinylcholine stimulates nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
Figure 13-5
Structural relationship of succinylcholine, a depolarizing
neuromuscular blocking agent, to acetylcholine. Succinylcholine consists of two
acetylcholine molecules linked through the acetate methyl groups. Like acetylcholine,
succinylcholine stimulates nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction.