VAPORIZERS
Through the years, vaporizers have evolved from rudimentary ether
inhalers and copper kettles to the present temperature-compensated, variable-bypass
vaporizers. In 1993, with the clinical introduction of desflurane, an even more
sophisticated vaporizer was introduced to handle the unique physical properties of
this agent. A
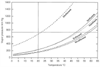 Figure 9-13
Vapor pressure versus temperature curves for desflurane,
isoflurane, halothane, enflurane, and sevoflurane. The vapor pressure curve for
desflurane is steeper and shifted to higher vapor pressures compared with the curves
for other contemporary inhaled anesthetics. (From inhaled anesthetic package
insert equations and from Susay SR, Smith MA, Lockwood GG: The saturated vapor pressure
of desflurane at various temperatures. Anesth Analg 83:864–866, 1996.)
Figure 9-13
Vapor pressure versus temperature curves for desflurane,
isoflurane, halothane, enflurane, and sevoflurane. The vapor pressure curve for
desflurane is steeper and shifted to higher vapor pressures compared with the curves
for other contemporary inhaled anesthetics. (From inhaled anesthetic package
insert equations and from Susay SR, Smith MA, Lockwood GG: The saturated vapor pressure
of desflurane at various temperatures. Anesth Analg 83:864–866, 1996.)
newer generation of anesthesia vaporizers blending the older, copper kettle-like
technology and innovative, computer-controlled technology has emerged in the Datex-Ohmeda
Aladin Cassette Vaporizer system. Before the discussion of variable-bypass vaporizers,
the Datex-Ohmeda Tec 6 desflurane vaporizer, and the Datex-Ohmeda Aladin cassette
vaporizer, certain physical principles are reviewed to facilitate understanding of
the operating principles, construction, and design of contemporary vaporizers.
Physics
Vapor Pressure
Contemporary inhaled volatile anesthetics exist in the liquid
state below 20°C. When a volatile liquid is in a closed container, molecules
escape from the liquid phase to the vapor phase until the number of molecules in
the vapor phase is constant. These molecules bombard the wall of the container and
create a pressure known as the saturated vapor pressure.
As the temperature increases, more molecules enter the vapor phase, and the vapor
pressure increases ( Fig. 9-13
).
Vapor pressure is independent of atmospheric pressure and is contingent only on
the temperature and physical characteristics of the liquid. The boiling point of
a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
[54]
[55]
[56]
At 760 mm Hg, the boiling points for desflurane, isoflurane, halothane, enflurane,
and sevoflurane are approximately 22.8°C, 48.5°C, 50.2°C, 56.5°C,
and 58.5°C, respectively. Unlike other contemporary inhaled anesthetics, desflurane
boils at temperatures that may be encountered in clinical settings such as pediatric
and burn operating rooms. This unique physical characteristic alone mandates a special
vaporizer design to control the delivery of desflurane. If agent-specific vaporizers
are inadvertently misfilled with incorrect liquid anesthetic agents, the resulting
mixtures of volatile agents may demonstrate unique properties from those of the individual
component agents.
The altered vapor pressure and other physical properties of the azeotropic mixtures
that result from mixing various agents may alter the output of the anesthetic vaporizer
[57]
(see "Misfilling").
Latent Heat of Vaporization
Energy must be expended to convert a molecule from the liquid
to gaseous state because the molecules of a liquid tend to cohere. The latent
heat of vaporization is defined as the number of calories required to
change 1 g of liquid into vapor without a temperature change. The energy for vaporization
must come from the liquid itself or from an outside source. The temperature of the
liquid decreases during vaporization in the absence of an outside energy source.
Energy loss can lead to significant decreases in temperature of the remaining liquid.
This temperature drop can greatly decrease vaporization.[54]
[56]
[58]
Specific Heat
The specific heat of a substance
is the number of calories required to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance
by 1°C.[45]
[49]
[54]
The substance can be solid, liquid, or gas.
The concept of specific heat is important to the design, operation, and construction
of vaporizers because it is applicable in two ways. First, the specific heat value
for an inhaled anesthetic is important because it indicates how much heat must be
supplied to the liquid to maintain a constant temperature when heat is lost during
vaporization. Second, manufacturers select vaporizer component metals that have
a high specific heat to minimize temperature changes associated with vaporization.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure
of the speed with which heat flows through a substance. The higher the thermal conductivity,
the better the substance conducts heat.[54]
Vaporizers
are constructed of metals that have relatively high thermal conductivity, which helps
maintain a uniform temperature.
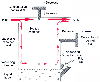 Figure 9-14
Generic variable-bypass vaporizer. Vaporizer components
include the concentration control dial, the bypass chamber, the vaporizing chamber,
the filler port, and the filler cap. Using the filler port, the operator fills the
vaporizing chamber with liquid anesthetic. The maximum safe fill level is predetermined
by the position of the filler port, which is positioned to minimize the chance of
overfilling. If a vaporizer is overfilled or tilted, liquid anesthetic can spill
into the bypass chamber, causing an overdose. The concentration control dial is
a variable restrictor, which can be located in the bypass chamber or the outlet of
the vaporizing chamber. The function of the concentration control dial is to regulate
the relative flow rates through the bypass and vaporizing chambers. (Modified
from Andrews JJ, Brockwell RC: Delivery systems for inhaled anesthetics. In
Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK [eds]: Clinical Anesthesia, 4th ed. New York,
Lippincott-Raven, 2000, pp 567–594.)
Figure 9-14
Generic variable-bypass vaporizer. Vaporizer components
include the concentration control dial, the bypass chamber, the vaporizing chamber,
the filler port, and the filler cap. Using the filler port, the operator fills the
vaporizing chamber with liquid anesthetic. The maximum safe fill level is predetermined
by the position of the filler port, which is positioned to minimize the chance of
overfilling. If a vaporizer is overfilled or tilted, liquid anesthetic can spill
into the bypass chamber, causing an overdose. The concentration control dial is
a variable restrictor, which can be located in the bypass chamber or the outlet of
the vaporizing chamber. The function of the concentration control dial is to regulate
the relative flow rates through the bypass and vaporizing chambers. (Modified
from Andrews JJ, Brockwell RC: Delivery systems for inhaled anesthetics. In
Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK [eds]: Clinical Anesthesia, 4th ed. New York,
Lippincott-Raven, 2000, pp 567–594.)
 |
 Figure 9-13
Vapor pressure versus temperature curves for desflurane,
isoflurane, halothane, enflurane, and sevoflurane. The vapor pressure curve for
desflurane is steeper and shifted to higher vapor pressures compared with the curves
for other contemporary inhaled anesthetics. (From inhaled anesthetic package
insert equations and from Susay SR, Smith MA, Lockwood GG: The saturated vapor pressure
of desflurane at various temperatures. Anesth Analg 83:864–866, 1996.)
Figure 9-13
Vapor pressure versus temperature curves for desflurane,
isoflurane, halothane, enflurane, and sevoflurane. The vapor pressure curve for
desflurane is steeper and shifted to higher vapor pressures compared with the curves
for other contemporary inhaled anesthetics. (From inhaled anesthetic package
insert equations and from Susay SR, Smith MA, Lockwood GG: The saturated vapor pressure
of desflurane at various temperatures. Anesth Analg 83:864–866, 1996.) Figure 9-14
Generic variable-bypass vaporizer. Vaporizer components
include the concentration control dial, the bypass chamber, the vaporizing chamber,
the filler port, and the filler cap. Using the filler port, the operator fills the
vaporizing chamber with liquid anesthetic. The maximum safe fill level is predetermined
by the position of the filler port, which is positioned to minimize the chance of
overfilling. If a vaporizer is overfilled or tilted, liquid anesthetic can spill
into the bypass chamber, causing an overdose. The concentration control dial is
a variable restrictor, which can be located in the bypass chamber or the outlet of
the vaporizing chamber. The function of the concentration control dial is to regulate
the relative flow rates through the bypass and vaporizing chambers. (Modified
from Andrews JJ, Brockwell RC: Delivery systems for inhaled anesthetics. In
Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK [eds]: Clinical Anesthesia, 4th ed. New York,
Lippincott-Raven, 2000, pp 567–594.)
Figure 9-14
Generic variable-bypass vaporizer. Vaporizer components
include the concentration control dial, the bypass chamber, the vaporizing chamber,
the filler port, and the filler cap. Using the filler port, the operator fills the
vaporizing chamber with liquid anesthetic. The maximum safe fill level is predetermined
by the position of the filler port, which is positioned to minimize the chance of
overfilling. If a vaporizer is overfilled or tilted, liquid anesthetic can spill
into the bypass chamber, causing an overdose. The concentration control dial is
a variable restrictor, which can be located in the bypass chamber or the outlet of
the vaporizing chamber. The function of the concentration control dial is to regulate
the relative flow rates through the bypass and vaporizing chambers. (Modified
from Andrews JJ, Brockwell RC: Delivery systems for inhaled anesthetics. In
Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK [eds]: Clinical Anesthesia, 4th ed. New York,
Lippincott-Raven, 2000, pp 567–594.)