Spinal Anesthesia
Spinal (subarachnoid) anesthesia offers many advantages for cesarean
delivery. It has a very rapid onset and provides a dense neural block. Because
of the small doses used, there is little risk of local anesthetic toxicity and minimal
transfer of drug to the fetus. In addition, failures (including incomplete or patchy
blocks) are very infrequent with spinal anesthesia. Disadvantages of this technique
include the finite duration of anesthesia and a higher incidence of hypotension.
Hyperbaric bupivacaine is the most commonly used agent for spinal
anesthesia when performing cesarean sections. Its duration of action of 1.5 to 2
hours is perfectly matched to the duration of surgery in most cases. Although some
authors have advocated a sliding scale of doses that depend on patient height, most
practitioners now use a set dose of hyperbaric bupivacaine.[168]
As noted in Figure 58-10
,
neither patient height, weight, nor body mass index appears to correlate with block
height.[168]
Although increasing the dose of spinal
anesthetic increases block height,[169]
doses above
15 mg significantly increase the risk of complications, including high block, and
are not recommended. Spinal hyperbaric bupivacaine is marketed in concentrations
of 0.5%, 0.75%, and 1%; however, availability varies from country to country. Although
the extent of the blockade does not appear to be greatly affected by concentration,
[170]
the density of the sensory block may be better
with the 0.75% than the 0.5% concentration. However, there seems to be little advantage
and potential disadvantage to use of the 1% concentration. A recent comparison of
0.75% with 1% bupivacaine found no difference in onset time or quality of block,
but an increased incidence of backache was reported in the 1% group.[171]
Spinal anesthesia can be initiated with the patient in either
the sitting or the lateral position and with either plain or hyperbaric solutions.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The sitting position, however,
appears to be optimal for placement of a neuraxial block in an obese parturient.
[172]
Hyperbaric solutions have the advantage of
greater predictability of block height than plain solutions do, and they allow the
anesthesiologist the ability to adjust block height by adjusting table position.
[173]
Despite achieving an adequate (T4) block, some women under spinal
anesthesia will experience some degree of visceral discomfort during cesarean section,
particularly in situations in which the obstetrician exteriorizes the uterus. The
quality of the spinal anesthesia has been
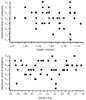 Figure 58-10
Relationship between patient weight and height and block
height during spinal anesthesia with 12 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine in 50 term parturients
undergoing cesarean section. Circles represent one
patient; squares, two patients; triangles,
three patients; and diamonds, four patients. (From
Shnider SM, Moya F: Effects of meperidine on the newborn infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol
89:1009–1015, 1964.)
Figure 58-10
Relationship between patient weight and height and block
height during spinal anesthesia with 12 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine in 50 term parturients
undergoing cesarean section. Circles represent one
patient; squares, two patients; triangles,
three patients; and diamonds, four patients. (From
Shnider SM, Moya F: Effects of meperidine on the newborn infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol
89:1009–1015, 1964.)
reported to be improved by the addition of epinephrine,[174]
morphine,[175]
fentanyl,[176]
or sufentanil.[177]
 Figure 58-10
Relationship between patient weight and height and block
height during spinal anesthesia with 12 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine in 50 term parturients
undergoing cesarean section. Circles represent one
patient; squares, two patients; triangles,
three patients; and diamonds, four patients. (From
Shnider SM, Moya F: Effects of meperidine on the newborn infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol
89:1009–1015, 1964.)
Figure 58-10
Relationship between patient weight and height and block
height during spinal anesthesia with 12 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine in 50 term parturients
undergoing cesarean section. Circles represent one
patient; squares, two patients; triangles,
three patients; and diamonds, four patients. (From
Shnider SM, Moya F: Effects of meperidine on the newborn infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol
89:1009–1015, 1964.)